Dell PowerVault TL4000 Dell PowerVault ML6000 Encryption Key Manager User's - Page 17
Library-Managed Tape Encryption, About Encryption Keys - specifications
 |
View all Dell PowerVault TL4000 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 17 highlights
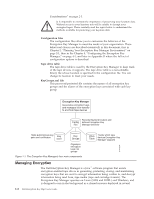
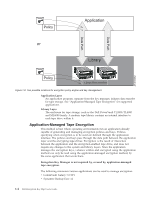
| Application-managed tape encryption is supported in LTO 4 and LTO 5 Tape Drives in: v Dell™ PowerVault™ TL2000 Tape Library v Dell™ PowerVault™ TL4000 Tape Library v Dell™ PowerVault™ ML6000 Tape Library See your tape backup software application documentation to learn how to manage encryption policies and keys. Library-Managed Tape Encryption | Use this method for LTO 4 and LTO 5 tape drives in the Dell™ PowerVault™ TL2000 Tape Library, Dell™ PowerVault™ TL4000 Tape Library, or Dell™ PowerVault™ ML6000 Tape Library. Key generation and management is performed by the Encryption Key Manager, a Java application running on a library-attached host. Policy control and keys pass through the library-to-drive interface, therefore encryption is transparent to the applications. About Encryption Keys An encryption key is a random string of bits generated specifically to scramble and unscramble data. Encryption keys are created using algorithms designed to ensure that each key is unique and unpredictable. The longer the key constructed this way, the harder it is to break the encryption code. Both the IBM and T10 methods of encryption use 256-bit AES algorithm keys to encrypt data. 256-bit AES is the encryption standard currently recognized and recommended by the U.S. government, which allows three different key lengths. 256-bit keys are the longest allowed by AES. Two types of encryption algorithms are used by the Encryption Key Manager: symmetric algorithms and asymmetric algorithms. Symmetric, or secret key encryption, uses a single key for both encryption and decryption. Symmetric key encryption is generally used for encrypting large amounts of data in an efficient manner. 256-bit AES keys are symmetric keys. Asymmetric, or public/private encryption, uses a pair of keys. Data encrypted using one key can only be decrypted using the other key in the public/private key pair. When an asymmetric key pair is generated, the public key is used to encrypt, and the private key is used to decrypt. The Encryption Key Manager uses both symmetric and asymmetric keys; symmetric encryption for high-speed encryption of user or host data, and asymmetric encryption (which is necessarily slower) for protecting the symmetric key. Encryption keys may be generated for the Encryption Key Manager by a utility such as keytool. The responsibility for generating AES keys and the manner in which they are transferred to the tape drive depends on the method of encryption management. However, it may be helpful to understand the difference between how the Encryption Key Manager uses encryption keys and how other applications use them. Encryption Key Processing by the Dell Encryption Key Manager | In library-managed tape encryption, unencrypted data is sent to the LTO 4 or LTO | 5 Tape Drive and converted to ciphertext using a pre-generated symmetric Data Key (DK) from a keystore available to the Encryption Key Manager, and is then Chapter 1. Tape Encryption Overview 1-5