Dell PowerVault TL4000 Dell PowerVault ML6000 Encryption Key Manager User's - Page 24
Encryption Keys and the LTO 4 and LTO 5 Tape Drives, Key Manager
 |
View all Dell PowerVault TL4000 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 24 highlights
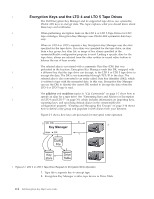
| Encryption Keys and the LTO 4 and LTO 5 Tape Drives The Dell Encryption Key Manager and its supported tape drives use symmetric, 256-bit AES keys to encrypt data. This topic explains what you should know about these keys and certificates. | When performing encryption tasks on the LTO 4 or LTO 5 Tape Drives for LTO tape cartridges, Encryption Key Manager uses 256-bit AES symmetric data keys only. | When an LTO 4 or LTO 5 requests a key, Encryption Key Manager uses the alias specified for the tape drive. If no alias was specified for the tape drive, an alias from a key group, key alias list, or range of key aliases specified in the symmetricKeySet configuration property is used. Lacking a specific alias for the tape drive, aliases are selected from the other entities in round robin fashion to balance the use of keys evenly. The selected alias is associated with a symmetric Data Key (DK) that was preloaded in the keystore. Encryption Key Manager sends this DK, wrapped with | a different key that the tape drive can decrypt, to the LTO 4 or LTO 5 tape drive to encrypt the data. The DK is not transmitted through TCP/IP in the clear. The selected alias is also converted to an entity called Data Key identifier (DKi), which is written to tape with the encrypted data. In this way, Encryption Key Manager can use the DKi to identify the correct DK needed to decrypt the data when the | LTO 4 or LTO 5 tape is read. The adddrive and moddrive topics in "CLI Commands" on page 5-7 show how to specify an alias for a tape drive. See "Generating Keys and Aliases for Encryption | on LTO 4 and LTO 5" on page 3-9, which includes information on importing keys, exporting keys, and specifying default aliases in the symmetricKeySet configuration property. "Creating and Managing Key Groups" on page 3-14 shows how to define a key group and populate it with aliases from your keystore. Figure 2-1 shows how keys are processed for encrypted write operation. 5 DK, DKi 6 7 Key Manager 3 alias DK 1 Config File 4 2 Key store Drive Table | Figure 2-1. LTO 4 or LTO 5 Tape Drive Request for Encryption Write Operation 1. Tape drive requests key to encrypt tape 2. Encryption Key Manager verifies tape device in Drive Table 2-4 Dell Encryption Key Mgr User's Guide