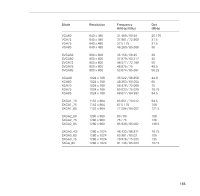
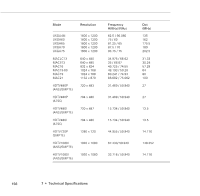
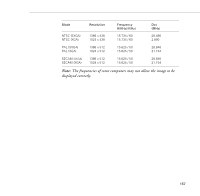
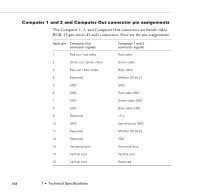
Epson PowerLite 9000NL User Manual - Page 170
NTSC., Point., Resolution., S-Video., SECAM, Sleep mode., used in Western Europe, India, China
 |
View all Epson PowerLite 9000NL manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 170 highlights
NTSC. A 525-line video broadcast format developed by the National Television Standards Committee. NTSC is widely used in North America, Mexico, and Japan. PAL (Phase Alternation by Line). A 625-line video broadcast format used in Western Europe, India, China, Australia, New Zealand, and parts of Africa. Point. A measurement of drawn or printed objects. One point equals 1/72 inch. Resolution. A measure of the amount of detail contained in an image. Resolution can be measured in dots per inch or in pixels. Image sharpness and clarity improve as resolution increases. RGB. A type of color scheme that defines color as percentages of red, green, and blue. S-Video. A type of video signal used in S-VHS videotape formats. It transmits luminance and color separately. SECAM (System Electronique pour Couleur Avec Memoire). A 625-line TV system used in France, Eastern Europe, Russia, and parts of Africa. Sleep mode. A power-saving feature in which the projection lamp is turned off when a video signal has not been applied for 30 minutes. In sleep mode, only a minimum amount of the projector's circuitry remains on. SVGA. Super Video Graphics Array. SVGA provides higher resolution than VGA (800 × 600). 160 Glossary