HP P4000 HP Smart Array SAS controllers for Integrity servers support guide - Page 109
A Physical disk installation and replacement, Overview
 |
View all HP P4000 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 109 highlights
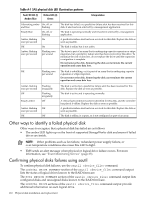
A Physical disk installation and replacement This appendix discusses the procedure for replacing physical disks in an array. Overview When a physical disk fails, the logical drive it belongs to is affected. Each logical drive connected to a Smart Array Controller can be configured with a different RAID level. Logical drives can be affected differently by a physical disk failure, depending on their configured RAID level. The effects of physical disk failure for each RAID level are: RAID 0 Cannot tolerate disk drive failure. If any physical disk in the array fails, the logical drive also fails. RAID 1 Tolerates one physical disk failure. RAID 1+0 Tolerates multiple physical disk failures if no failed disks are mirrored to one another. RAID 5 Tolerates one physical disk failure. RAID 50 Tolerates one physical disk failure per RAID 5 parity group. RAID ADG Tolerates simultaneous failure of two physical disks. RAID 60 Tolerates simultaneous failure of two physical disks per RAID ADG parity group. If more physical disks fail than the RAID level supports, fault tolerance is compromised and the logical drive fails. All requests from the operating system are rejected with unrecoverable errors. For steps to recover from this situation, see "Compromised fault tolerance" (page 111). SAS physical disk failure indicators (for internal disks connected to Smart Array controllers) The LEDs on the front of each physical disk are visible through the front of the server. When a physical disk is configured as part of an array and is attached to a powered-on controller, you can determine the status of the disk from the illumination pattern of the LEDs. Figure A-1 SAS Physical Disk Status LED Indicators 1 2 Overview 109