HP t505 Administrator Guide - Page 50
Using multi-monitor sessions with RDP, Using multimedia redirection with RDP
 |
View all HP t505 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 50 highlights
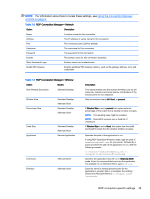
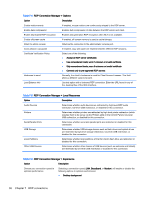
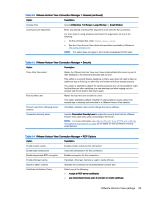
NOTE: Some Windows RDP servers will not send RemoteFX content to clients enabled for RDP 7.1 without a change to Group Policy. Check the setting of the following policy: Local Computer Policy > Computer Configuration > Administrative Templates > Windows Components > Remote Desktop Services > Remote Desktop Session Host > Remote Session Environment > Enable RemoteFX encoding for RemoteFX clients designed for Windows Server 2008 R2 SP1 In addition, Windows Server 2012 and Windows Server 2012 R2 require the following setting to be set to 32-bit: Local Computer Policy > Computer Configuration > Administrative Templates > Windows Components > Remote Desktop Services > Remote Desktop Session Host > Remote Session Environment > Limit maximum color depth Using multi-monitor sessions with RDP True multi-monitor support does not require special configuration. The RDP client automatically identifies which monitor is specified as the primary monitor in the local settings and places the taskbar and desktop icons on that monitor. When a window is maximized within the remote session, the window will only cover the monitor it was maximized on. Display preferences and monitor resolutions can be viewed but not modified within the remote session. To modify the session resolution, log out of the session and change the resolution on the local client. By default, all RDP sessions will be full-screen and cover all monitors to enhance the virtualization experience. Additional window options are available in the RDP Connection Manager. NOTE: Remote Desktop Virtualization Host (RDVH) sessions with graphics card support might only support certain resolutions and counts of monitors. The limits are specified when the RemoteFX virtual graphics device is configured for the RDVH virtual machine. Using multimedia redirection with RDP Multimedia redirection (MMR) is a technology that integrates with Windows Media Player on the remote host and streams the encoded media to the client instead of playing it on the remote host and re-encoding it via RDP. This technology reduces the server load and network traffic, and greatly improves the multimedia experience, supporting 24 fps playback of 1080p videos with automatic audio syncing. MMR is enabled by default. A client will negotiate with any RDP server it contacts, and if MMR is available, it will be used. MMR also uses an advanced codec detection scheme that identifies whether the client supports the codec being requested by the remote host before attempting to redirect it. The result is that only supported codecs will be redirected and all unsupported codecs fall back to server-side rendering. To disable MMR on the client for all RDP connections, set the following registry key to 0: root/ConnectionType/freerdp/general/enableMMR Because RemoteFX already delivers acceptable multimedia performance, you can disable MMR with RFX by setting the following registry key to 1: root/ConnectionType/freerdp/connections//disableMMRwithRFX TIP: For simplified management, HP recommends that MMR be enabled or disabled on the remote host. 38 Chapter 7 RDP connections