Honeywell HPF24S8 Installation Instructions - Page 39
How to Calculate System Current Draw
 |
View all Honeywell HPF24S8 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 39 highlights
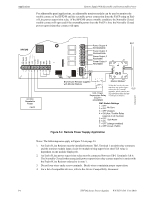
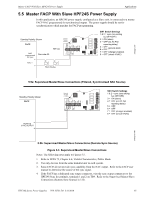
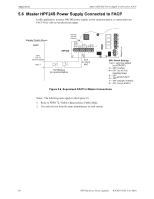
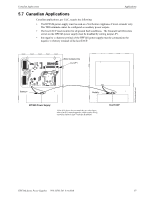
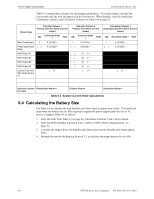
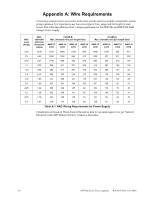
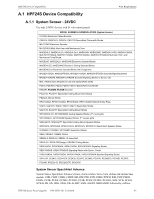
Calculating the System Current Draw Power Supply Requirements • Secondary refers to the power supply's backup batteries. • All currents are given in amperes (A). Table 6.2 shows how to convert milliamperes and microamperes to full amperes. To convert... Multiply Example Milliamperes (mA) to amperes (A) mA x 0.001 3 mA x 0.001 - 0.003 A Microamperes (A) to amperes (A) A x 0.000001 300 A x 0.000001 = 0.0003 A Table 6.2 Converting to Full Amperes 6.3.2 How to Calculate System Current Draw Use Table 6.3 on page 40 to calculate current draws as follows: 1. Enter the quantity of devices in all three columns. 2. Enter the current draw where required. Refer to the Device Compatibility Document for compatible devices and their current draw. 3. Calculate the current draws for each in all columns. 4. Sum the total current for each column. 5. Copy the totals from Column 2 and Column 3 to Table 6.3 on page 40. Following are the types of current that can be entered into Table 6.3 on page 40 - Calculation Column 1 - The primary supply current load that the power supply must support during a non-fire alarm condition, with AC power applied - Calculation Column 2 - The primary supply current load the power supply must support during a fire alarm condition, with AC power applied - Calculation Column 3 - The standby current drawn from the batteries in a non-fire alarm condition during a loss of AC power HPF24S Series Power Supplies - P/N 52751:D3 5/11/2010 39