Epson PowerLite Pro Z8150NL User Manual - Page 207
Glossary, WPS Wi-Fi Protected Set
 |
View all Epson PowerLite Pro Z8150NL manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
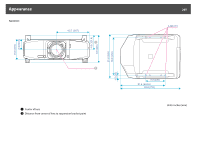
Page 207 highlights
Glossary 207 SVGA A type of video signal with a resolution of 800 (horizontal) ^ 600 (vertical) dots that is used by IBM PC/AT-compatible computers. SXGA A type of video signal with a resolution of 1,280 (horizontal) ^ 1,024 (vertical) dots that is used by IBM PC/AT-compatible computers. VGA A type of video signal with a resolution of 640 (horizontal) ^ 480 (vertical) dots that is used by IBM PC/AT-compatible computers. WPS (Wi-Fi Protected Set- Wi-Fi Protected Setup has been devised by the Wi-Fi Alliance as a means of easily setting up and securing a wireless LAN. up) XGA A type of video signal with a resolution of 1,024 (horizontal) ^ 768 (vertical) dots that is used by IBM PC/AT-compatible computers. Aspect Ratio (Aspect Ratio) The ratio between an image's length and its height. HDTV images have an aspect ratio of 16:9 and appear elongated. The aspect ratio for standard images is 4:3. Ad hoc mode A method of wireless LAN connection that communicates with wireless LAN clients without using an access point. Interlace A method of image scanning whereby the image data is divided into fine horizontal lines that are displayed in sequence starting from left to right and then from top to bottom. The even-numbered lines and odd-numbered lines are displayed alternately. Infrastructure mode A method for wireless LAN connection in which devices communicate through access points. Gateway address This is a server (router) for communicating across a network (subnet) divided according to subnet masksg. (Gateway Address) Contrast The relative brightness of the light and dark areas of an image can be increased or decreased to make text and graphics stand out more clearly, or to make them appear softer. Adjusting this particular property of an image is called Contrast adjustment. Component Video A Video signal which has the luminance component and color component separated to provide better image quality. Refers to images that consist of three independent signals: Y (luminance signal), Pb and Pr (color difference signals). Composite video Video signals that have the video brightness signals and color signals mixed together. The type of signals commonly used by household video equipment (NTSC, PAL, and SECAM formats). The carrier signal Y (luminance signal) and chroma (color) signal that are contained in the color bar are overlapped to form a single signal. Subnet mask (Subnet Mask) This is a numerical value that defines the number of bits used for the network address on a divided network (subnet) from the IP Addressg. Sync. The signals output from computers have a specific frequency. If the projector frequency does not match this frequency, the resulting images are not of a good quality. The process of matching the phases of these signals (the relative position of the crests and the troughs in the signal) is called Synchronization. If the signals are not synchronized, flickering, blurriness, and horizontal interference occur.