Garmin G500 Pilots Guide - Page 194
Radar Signal Reflectivity
 |
View all Garmin G500 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 194 highlights
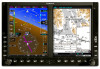
Foreword System Sec 1 PFD Sec 2 Attenuation can also be due to poor maintenance or degradation of the radome. Even the smallest amount of wear and tear, pitting, and pinholes on the radome surface can cause damage and system inefficiency. 4.8.2 Radar Signal Reflectivity 4.8.2.1 Precipitation Precipitation or objects more dense than water, such as earth or solid structures, will be detected by the weather radar. The weather radar will not detect clouds, thunderstorms or turbulence directly. It detects precipitation associated with clouds, thunderstorms, and turbulence. The best radar signal reflectors are raindrops, wet snow or wet hail. The larger the raindrop the better it reflects. The size of the precipitation droplet is the most important factor in radar reflectivity. Because large drops in a small concentrated area are characteristic of a severe thunderstorm, the radar displays the storm as a strong return. Ice, dry snow, and dry hail have low reflective levels and often will not be displayed by the radar. A cloud that contains only small raindrops, such as fog or drizzle, will not reflect enough radar energy to produce a measurable target return. MFD Sec 3 Features Avoidance Hazard Sec 4 Additional Sec 5 & Alerts Annun. Sec 6 Symbols Sec 7 Appendix A Glossary Sec 8 Index Appendix B Figure 4-57 Precipitation Type and Reflectivity 4-66 Garmin G500 Pilot's Guide 190-01102-02 Rev. B















