D-Link DSN-6410 User Manual for DSN-6410 - Page 10
RAID levels
 |
View all D-Link DSN-6410 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 10 highlights
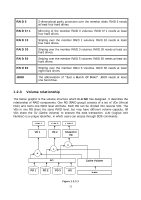
MPIO MC/S MTU CHAP iSNS Multi-Path Input/Output. Multiple Connections per Session Maximum Transmission Unit. Challenge Handshake Authentication Protocol. An optional security mechanism to control access to an iSCSI storage system over the iSCSI data ports. Internet Storage Name Service. • Part 3: Dual controller SBB Storage Bridge Bay. The objective of the Storage Bridge Bay Working Group (SBB) is to create a specification that defines mechanical, electrical and low-level enclosure management requirements for an enclosure controller slot that will support a variety of storage controllers from a variety of independent hardware vendors ("IHVs") and system vendors. • Part 4: 10GbE SFP+ CX4 Small Form-factor Pluggable is a compact, hot-pluggable transceiver used for both Fibre Channel and 10GbE. 10GBASE-CX4, a copper based 10 Gigabit Ethernet PHY. 1.2.2 RAID levels There are different RAID levels with different degree of data protection, data availability, and performance to host environment. The description of RAID levels are on the following: RAID 0 Disk striping. RAID 0 needs at least one hard drive. RAID 1 Disk mirroring over two disks. RAID 1 needs at least two hard drives. N-way mirror Extension to RAID 1 level. It has N copies of the disk. RAID 3 Striping with parity on the dedicated disk. RAID 3 needs at least three hard drives. RAID 5 Striping with interspersed parity over the member disks. RAID 3 needs at least three hard drives. 10