D-Link DSN-6410 User Manual for DSN-6410 - Page 95
Disk roaming, VD clone
 |
View all D-Link DSN-6410 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 95 highlights
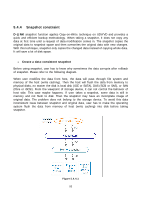
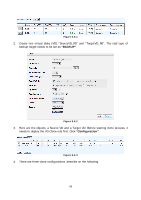
When a snapshot has been rollbacked, the other snapshots which are earlier than it will also be removed. But the rest snapshots will be kept after rollback. If a snapshot has been deleted, the other snapshots which are earlier than it will also be deleted. The space occupied by these snapshots will be released after deleting. 5.5 Disk roaming Physical disks can be re-sequenced in the same system or move all physical disks in the same RAID group from system-1 to system-2. This is called disk roaming. System can execute disk roaming online. Please follow the procedures. 1. Select "/ Volume configuration / RAID group". 2. Check the gray button next to the RG number; click "Deactivate". 3. Move all PDs of the RG to another system. 4. Check the gray button next to the RG number; click "Activate". 5. Done. Disk roaming has some constraints as described in the followings: 1. Check the firmware version of two systems first. It is better that either both systems have the same firmware version or system-2 firmware version is newer. 2. All physical disks of the RG should be moved from system-1 to system-2 together. The configuration of both RG and VD will be kept but LUN configuration will be cleared in order to avoid conflict with system-2's original setting. 5.6 VD clone The user can use VD clone function to backup data from source VD to target VD, set up backup schedule, and deploy the clone rules. The procedures of VD clone are on the following: 1. Copy all data from source VD to target VD at the beginning (full copy). 2. Use Snapshot technology to perform the incremental copy afterwards. Please be fully aware that the incremental copy needs to use snapshot to compare the data difference. Therefore, the enough snapshot space for VD clone is very important. The following contents will take an example of a RAID 5 virtual disk (SourceVD_Raid5) clone to RAID 6 virtual disk (TargetVD_Raid6). • Start VD clone 1. Create a RAID group (RG) in advance. 95