D-Link DSN-6410 User Manual for DSN-6410 - Page 93
Snapshot constraint
 |
View all D-Link DSN-6410 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 93 highlights
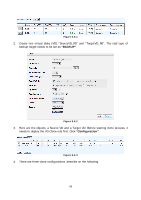
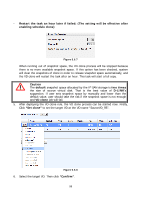
5.4.4 Snapshot constraint D-LINK snapshot function applies Copy-on-Write technique on UDV/VD and provides a quick and efficient backup methodology. When taking a snapshot, it does not copy any data at first time until a request of data modification comes in. The snapshot copies the original data to snapshot space and then overwrites the original data with new changes. With this technique, snapshot only copies the changed data instead of copying whole data. It will save a lot of disk space. • Create a data-consistent snapshot Before using snapshot, user has to know why sometimes the data corrupts after rollback of snapshot. Please refer to the following diagram. When user modifies the data from host, the data will pass through file system and memory of the host (write caching). Then the host will flush the data from memory to physical disks, no matter the disk is local disk (IDE or SATA), DAS (SCSI or SAS), or SAN (fibre or iSCSI). From the viewpoint of storage device, it can not control the behavior of host side. This case maybe happens. If user takes a snapshot, some data is still in memory and not flush to disk. Then the snapshot may have an incomplete image of original data. The problem does not belong to the storage device. To avoid this data inconsistent issue between snapshot and original data, user has to make the operating system flush the data from memory of host (write caching) into disk before taking snapshot. Figure 5.4.4.1 93