D-Link DSN-6410 User Manual for DSN-6410 - Page 8
RAID concepts
 |
View all D-Link DSN-6410 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 8 highlights
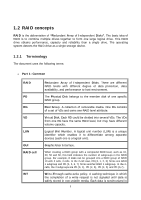
1.2 RAID concepts RAID is the abbreviation of "Redundant Array of Independent Disks". The basic idea of RAID is to combine multiple drives together to form one large logical drive. This RAID drive obtains performance, capacity and reliability than a single drive. The operating system detects the RAID drive as a single storage device. 1.2.1 Terminology The document uses the following terms: • Part 1: Common RAID PD RG VD LUN GUI RAID cell WT Redundant Array of Independent Disks. There are different RAID levels with different degree of data protection, data availability, and performance to host environment. The Physical Disk belongs to the member disk of one specific RAID group. Raid Group. A collection of removable media. One RG consists of a set of VDs and owns one RAID level attribute. Virtual Disk. Each RD could be divided into several VDs. The VDs from one RG have the same RAID level, but may have different volume capacity. Logical Unit Number. A logical unit number (LUN) is a unique identifier which enables it to differentiate among separate devices (each one is a logical unit). Graphic User Interface. When creating a RAID group with a compound RAID level, such as 10, 30, 50 and 60, this field indicates the number of subgroups in the RAID group. For example, 8 disks can be grouped into a RAID group of RAID 10 with 2 cells, 4 cells. In the 2-cell case, PD {0, 1, 2, 3} forms one RAID 1 subgroup and PD {4, 5, 6, 7} forms another RAID 1 subgroup. In the 4cells, the 4 subgroups are PD {0, 1}, PD {2, 3}, PD {4, 5} and PD {6,7}. Write-Through cache-write policy. A caching technique in which the completion of a write request is not signaled until data is safely stored in non-volatile media. Each data is synchronized in 8