D-Link DSN-6410 User Manual for DSN-6410 - Page 63
Used snapshot space / Total snapshot space
 |
View all D-Link DSN-6410 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 63 highlights
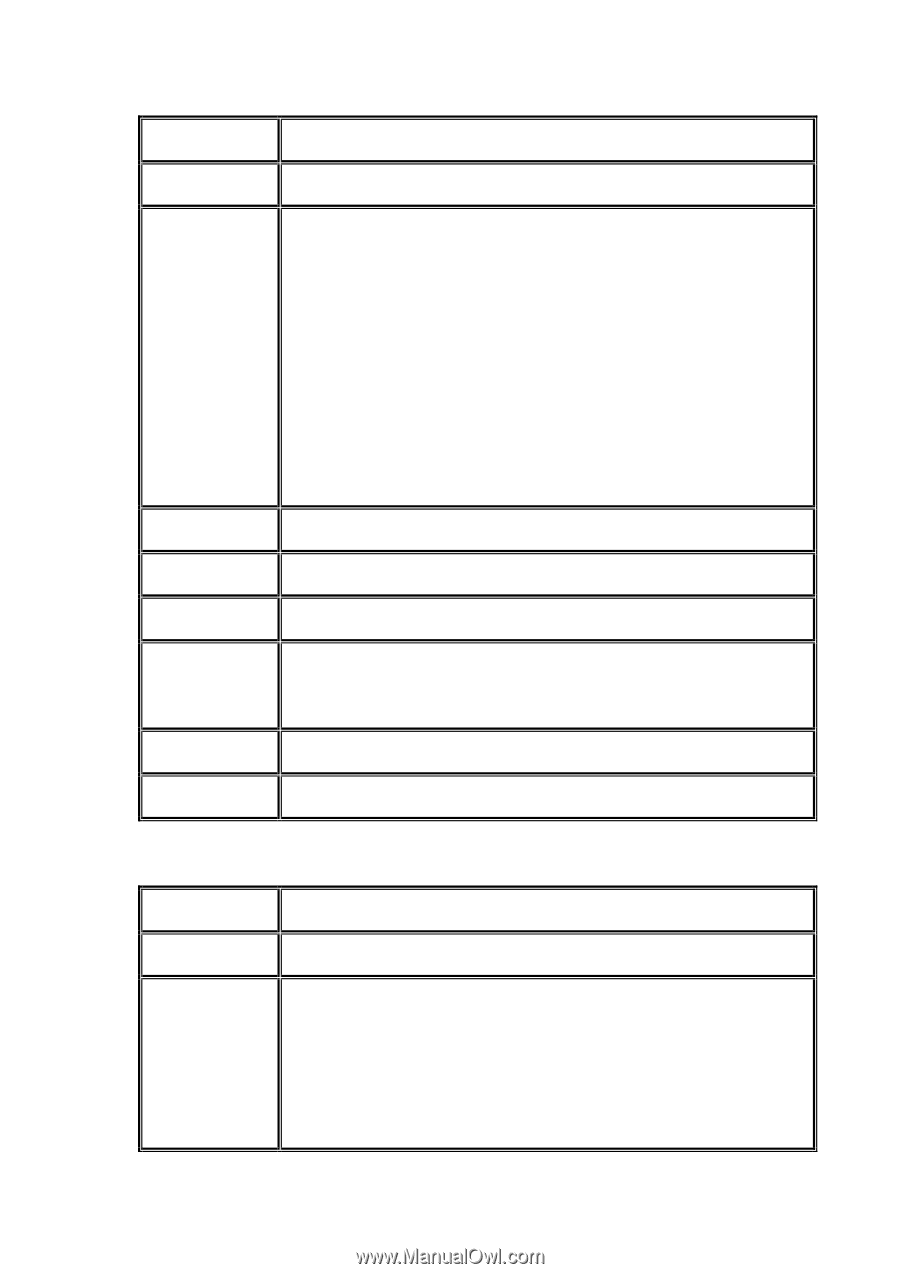
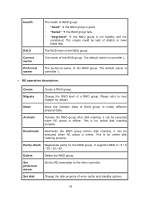
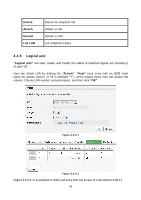
Clone Schedule Health R % RAID #LUN Snapshot (GB) (MB) #Snapshot RG name The target name of virtual disk. The clone schedule of virtual disk: The health of virtual disk: "Optimal" the virtual disk is working well and there is no failed disk in the RG. "Degraded" At least one disk from the RG of the Virtual disk is failed or plugged out. "Failed" the RAID group disk of the VD has single or multiple failed disks than its RAID level can recover from data loss. "Partially optimal" the virtual disk has experienced recoverable read errors. After passing parity check, the health will become "Optimal". Ratio (%) of initializing or rebuilding. RAID level. Number of LUN(s) that virtual disk is attached to. The virtual disk size that is used for snapshot. The number means "Used snapshot space" / "Total snapshot space". The unit can be displayed in GB or MB. Number of snapshot(s) that have been taken. The RG name of the virtual disk • VD operation description: Create Create a virtual disk. Extend Extend the virtual disk capacity. Parity check Execute parity check for the virtual disk. It supports RAID 3 / 5 / 6 / 30 / 50 / 60. Regenerate parity: "Yes" Regenerate RAID parity and write. "No" Execute parity check only and find mismatches. It will stop checking when mismatches count to 1 / 10 / 20 63