HP 6125XLG R2306-HP 6125XLG Blade Switch IP Multicast Configuration Guide - Page 126
assume that IPv6 unicast routes are available in the network, and IPv6 multicast
 |
View all HP 6125XLG manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 126 highlights
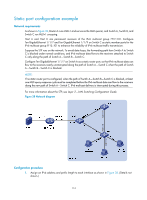
multicast routing entry and an IPv6 multicast forwarding entry for an IPv6 multicast packet, it sets the RPF interface of the packet as the incoming interface of the forwarding entry. After the router receives an IPv6 multicast packet, it searches its IPv6 multicast forwarding table: • If no forwarding entry matches the packet, the packet undergoes an RPF check. The router creates an IPv6 multicast routing entry with the RPF interface as the incoming interface and installs the entry into the IPv6 multicast forwarding table. { If the interface that received the packet is the RPF interface, the RPF check succeeds and the router forwards the packet out of all outgoing interfaces. { If the interface that received the packet is not the RPF interface, the RPF check fails and the router discards the packet. • If a forwarding entry matches the packet, and the interface that received the packet is the incoming interface of the forwarding entry, the router forwards the packet out of all outgoing interfaces. • If a forwarding entry matches the packet, but the interface that received the packet is not the incoming interface of the forwarding entry, the IPv6 multicast packet undergoes an RPF check. { If the RPF interface is the incoming interface, it means that the forwarding entry is correct but the packet traveled along a wrong path. The router discards the packet. { If the RPF interface is not the incoming interface, it means that the forwarding entry has expired, and the router replaces the incoming interface with the RPF interface. If the interface that received the packet is the RPF interface, the router forwards the packet out of all outgoing interfaces. Otherwise, it discards the packet. Figure 39 RPF check process IPv6 Routing Table on Switch C Destination/Prefix Interface 2000::/16 Vlan-int20 Source Switch B Receiver Vlan-int10 2000::101/16 Switch A Vlan-int20 Vlan-int10 IPv6 Multicast packets Switch C Receiver As shown in Figure 39, assume that IPv6 unicast routes are available in the network, and IPv6 multicast packets travel along the SPT from the multicast source to the receivers. The IPv6 multicast forwarding table on Switch C contains the (S, G) entry, with VLAN-interface 20 as the RPF interface. • When VLAN-interface 20 of Switch C receives an IPv6 multicast packet, because the interface is the incoming interface of the (S, G) entry, the router forwards the packet out of all outgoing interfaces. • When VLAN-interface 10 of Switch C receives an IPv6 multicast packet, because the interface is not the incoming interface of the (S, G) entry, the router performs an RPF check on the packet. The router searches its IPv6 unicast routing table and finds that the outgoing interface to the source (the RPF interface) is VLAN-interface 20. This means that the (S, G) entry is correct but the packet traveled along a wrong path. The RPF check fails and the router discards the packet. 119