HP 6125XLG R2306-HP 6125XLG Blade Switch IP Multicast Configuration Guide - Page 57
IGMP queries and reports, on the routers generates *, G1 and *
 |
View all HP 6125XLG manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 57 highlights
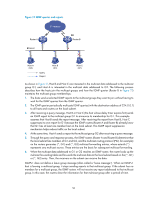
Figure 21 IGMP queries and reports IP network Router A DR Router B Ethernet Host A (G2) Query Report Host B (G1) Host C (G1) As shown in Figure 21, Host B and Host C are interested in the multicast data addressed to the multicast group G1, and Host A is interested in the multicast data addressed to G2. The following process describes how the hosts join the multicast groups and how the IGMP querier (Router B in Figure 21) maintains the multicast group memberships: 1. The hosts send unsolicited IGMP reports to the multicast groups they want to join without having to wait for the IGMP queries from the IGMP querier. 2. The IGMP querier periodically multicasts IGMP queries (with the destination address of 224.0.0.1) to all hosts and routers on the local subnet. 3. After receiving a query message, Host B or Host C (the host whose delay timer expires first) sends an IGMP report to the multicast group G1 to announce its membership for G1. This example assumes that Host B sends the report message. After receiving the report from Host B, Host C suppresses its own report for G1 because the IGMP routers (Router A and Router B) already know that G1 has at least one member host on the local subnet. This IGMP report suppression mechanism helps reduce traffic on the local subnet. 4. At the same time, Host A sends a report to the multicast group G2 after receiving a query message. 5. Through the query and response process, the IGMP routers (Router A and Router B) determine that the local subnet has members of G1 and G2, and the multicast routing protocol (PIM, for example) on the routers generates (*, G1) and (*, G2) multicast forwarding entries, where asterisk (*) represents any multicast source. These entries are the basis for subsequent multicast forwarding. 6. When the multicast data addressed to G1 or G2 reaches an IGMP router, the router looks up the multicast forwarding table and forwards the multicast data to the local subnet based on the (*, G1) or (*, G2) entry. Then, the receivers on the subnet can receive the data. IGMPv1 does not define a leave group message (often called a "leave message"). When an IGMPv1 host is leaving a multicast group, it stops sending reports to that multicast group. If the subnet has no members for a multicast group, the IGMP routers will not receive any report addressed to that multicast group. In this case, the routers clear the information for that multicast group after a period of time. 50