HP 6125XLG R2306-HP 6125XLG Blade Switch IP Multicast Configuration Guide - Page 49
Verifying the configuration, Creating an RPF route, Network requirements
 |
View all HP 6125XLG manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 49 highlights
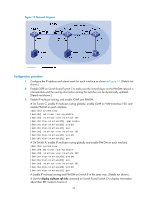
[SwitchA] interface vlan-interface 102 [SwitchA-Vlan-interface102] pim dm [SwitchA-Vlan-interface102] quit [SwitchA] interface vlan-interface 103 [SwitchA-Vlan-interface103] pim dm [SwitchA-Vlan-interface103] quit # Enable IP multicast routing and PIM-DM on Switch C in the same way. (Details not shown.) # Use the display multicast rpf-info command to display the RPF route to the source on Switch B. [SwitchB] display multicast rpf-info 50.1.1.100 RPF information about source 50.1.1.100: RPF interface: Vlan-interface102, RPF neighbor: 30.1.1.2 Referenced route/mask: 50.1.1.0/24 Referenced route type: igp Route selection rule: preference-preferred Load splitting rule: disable The output shows that the current RPF route on Switch B is contributed by a unicast routing protocol and the RPF neighbor is Switch A. 4. Configure a static multicast route on Switch B, specifying Switch C as its RPF neighbor on the route to the source. [SwitchB] ip rpf-route-static 50.1.1.100 24 20.1.1.2 Verifying the configuration Use the display multicast rpf-info command on Switch B to display information about the RPF route to the source. [SwitchB] display multicast rpf-info 50.1.1.100 RPF information about source 50.1.1.100: RPF interface: Vlan-interface101, RPF neighbor: 20.1.1.2 Referenced route/mask: 50.1.1.0/24 Referenced route type: multicast static Route selection rule: preference-preferred Load splitting rule: disable The output shows that: • The RPF route on Switch B is the configured static multicast route. • The RPF neighbor of Switch B is Switch C. Creating an RPF route Network requirements As shown in Figure 19, PIM-DM runs in the network and all switches in the network support IP multicast. Switch B and Switch C run OSPF, and have no unicast routes to Switch A. Typically, the receiver host receives the multicast data from Source 1 in the OSPF domain. Perform the configuration so that the receiver host receives multicast data from Source 2, which is outside the OSPF domain. 42