HP 6125XLG R2306-HP 6125XLG Blade Switch IP Multicast Configuration Guide - Page 56
Configuring IGMP, Overview, IGMPv1 overview
 |
View all HP 6125XLG manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 56 highlights
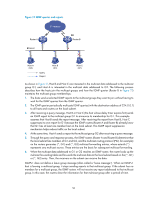
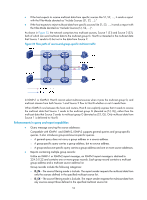
Configuring IGMP Overview Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP) establishes and maintains the multicast group memberships between a Layer 3 multicast device and its directly connected hosts. IGMP has three versions: • IGMPv1 (defined by RFC 1112) • IGMPv2 (defined by RFC 2236) • IGMPv3 (defined by RFC 3376) All IGMP versions support the ASM model. In addition to the ASM model, IGMPv3 can directly implement the SSM model. IGMPv1 and IGMPv2 must work with the IGMP SSM mapping function to implement the SSM model. For more information about the ASM and SSM models, see "Multicast overview." IGMPv1 overview IGMPv1 manages multicast group memberships based on the query and response mechanism. All routers that run IGMP on the same subnet can get IGMP membership report messages (often called "reports") from hosts, but the subnet needs only one router to act as the IGMP querier to send IGMP query messages (often called "queries"). The querier election mechanism determines which router acts as the IGMP querier on the subnet. In IGMPv1, the designated router (DR) elected by the multicast routing protocol (such as PIM) serves as the IGMP querier. For more information about DR, see "Configuring PIM." 49