HP 6125XLG R2306-HP 6125XLG Blade Switch IP Multicast Configuration Guide - Page 127
IPv6 multicast forwarding across IPv6 unicast subnets, Configuration task list
 |
View all HP 6125XLG manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 127 highlights
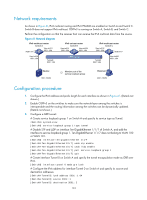
IPv6 multicast forwarding across IPv6 unicast subnets Routers forward the IPv6 multicast data from an IPv6 multicast source hop by hop along the forwarding tree, but some routers might not support IPv6 multicast protocols in a network. When the IPv6 multicast data is forwarded to a router that does not support IPv6 multicast, the forwarding path is blocked. In this case, you can enable IPv6 multicast data forwarding across the IPv6 unicast subnets by establishing a tunnel between the routers at both ends of the IPv6 unicast subnets. Figure 40 IPv6 multicast data transmission through a tunnel As shown in Figure 40, with a tunnel established between the multicast routers Switch A and Switch B, Switch A encapsulates the IPv6 multicast data in unicast IPv6 packets, and forwards them to Switch B across the tunnel through unicast routers. Then, Switch B strips off the unicast IPv6 header and continues to forward the IPv6 multicast data down toward the receivers. Configuration task list Tasks at a glance (Required.) Enabling IPv6 multicast routing (Optional.) Configuring IPv6 multicast routing and forwarding • (Optional.) Configuring the RPF route selection rule • (Optional.) Configuring IPv6 multicast load splitting • (Optional.) Configuring an IPv6 multicast forwarding boundary • (Optional.) Configuring IPv6 static multicast MAC address entries Enabling IPv6 multicast routing Before you configure any Layer 3 IPv6 multicast functionality, you must enable IPv6 multicast routing. To enable IPv6 multicast routing: Step 1. Enter system view. Command system-view Remarks N/A 120