HP 6125XLG R2306-HP 6125XLG Blade Switch IP Multicast Configuration Guide - Page 73
Multicast source registration,
 |
View all HP 6125XLG manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 73 highlights
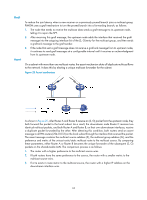
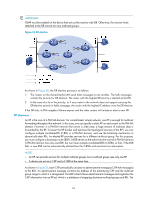
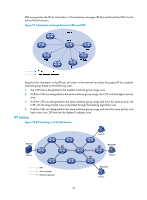
As shown in Figure 28, the process of building an RPT is as follows: 1. When a receiver wants to join the multicast group G, it uses an IGMP message to inform the receiver-side DR. 2. After getting the receiver information, the DR sends a join message, which is forwarded hop by hop to the RP that provides services for the multicast group. 3. The routers along the path from the DR to the RP form an RPT branch. Each router on this branch adds to its forwarding table a (*, G) entry, where the asterisk (*) means any multicast source. The RP is the root of the RPT, and the DR is a leaf of the RPT. When the multicast data addressed to the multicast group G reaches the RP, the RP forwards the data to the DR along the established RPT, and finally to the receiver. When a receiver is no longer interested in the multicast data addressed to the multicast group G, the receiver-side DR sends a prune message, which goes hop by hop along the RPT to the RP. After receiving the prune message, the upstream node deletes the interface that connects to this downstream node from the outgoing interface list and determines whether it has receivers for that multicast group. If not, the router continues to forward the prune message to its upstream router. Multicast source registration The multicast source uses the registration process to inform an RP of its presence. Figure 29 Multicast source registration As shown in Figure 29, the multicast source registers with the RP as follows: 1. The multicast source S sends the first multicast packet to the multicast group G. When receiving the multicast packet, the source-side DR encapsulates the packet in a PIM register message and unicasts the message to the RP. 2. After the RP receives the register message, it decapsulates the register message and forwards the register message down to the RPT. Meanwhile, it sends an (S, G) source-specific join message hop by hop toward the multicast source. The routers along the path from the RP to the multicast source constitute an SPT branch, and each router on this branch creates an (S, G) entry in its forwarding table. 3. The subsequent multicast data from the multicast source are forwarded to the RP along the established branch, and the RP forwards the data to the receivers along the RPT. When the 66