HP 6125XLG R2306-HP 6125XLG Blade Switch IP Multicast Configuration Guide - Page 136
Joining an IPv6 multicast group, MLD queries and reports
 |
View all HP 6125XLG manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 136 highlights
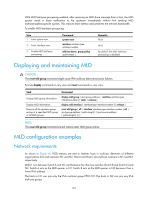
Joining an IPv6 multicast group Figure 42 MLD queries and reports IPv6 network Router A Ethernet Querier Router B Host A (G2) Query Report Host B (G1) Host C (G1) As shown in Figure 42, assume that Host B and Host C want to receive the IPv6 multicast data addressed to IPv6 multicast group G1, and Host A wants to receive the IPv6 multicast data addressed to G2. The following process describes how the hosts join the IPv6 multicast groups and how the MLD querier (Router B in Figure 42) maintains the IPv6 multicast group memberships: 1. The hosts send unsolicited MLD reports to the IPv6 multicast groups they want to join without having to wait for the MLD queries from the MLD querier. 2. The MLD querier periodically multicasts MLD queries (with the destination address FF02::1) to all hosts and routers on the local subnet. 3. After receiving a query, Host B or Host C (the delay timer of whichever expires first) sends an MLD report to the IPv6 multicast group G1 to announce its membership for G1. Assume that Host B sends the report. After hearing the report from Host B, Host C, which is on the same subnet as Host B, suppresses its own report for G1 because the MLD routers (Router A and Router B) already know that at least one host on the local subnet is interested in G1. This mechanism, known as the "MLD report suppression," helps reduce traffic on the local subnet. 4. At the same time, because Host A is interested in G2, it sends a report to the IPv6 multicast group G2. 5. Through the query/report process, the MLD routers learn that G1 and G2 have members on the local subnet, and the IPv6 multicast routing protocol (for example, IPv6 PIM) that is running on the routers generates (*, G1) and (*, G2) multicast forwarding entries. These entries are the basis for subsequent IPv6 multicast forwarding. The asterisk (*) represents any IPv6 multicast source. 6. When the IPv6 multicast data addressed to G1 or G2 reaches an MLD router, the router forwards the IPv6 multicast data to the local subnet according to the (*, G1) and (*, G2) multicast forwarding entries, and then the receivers on the subnet receive the data. Leaving an IPv6 multicast group When a host leaves a multicast group, the following process occurs: 129