HP GbE2c HP GbE2c Ethernet Blade Switch for c-Class BladeSystem Browser-based - Page 179
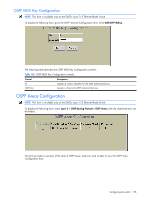
OSPF Area Configuration - ethernet blade switch default password
 |
UPC - 808736802215
View all HP GbE2c manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 179 highlights
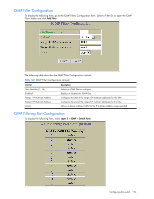
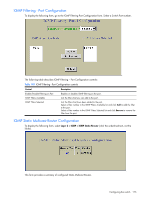
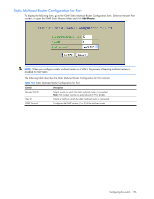
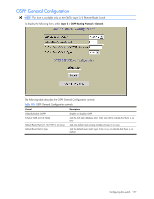
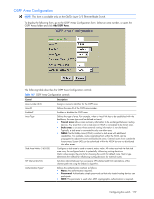
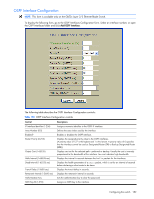
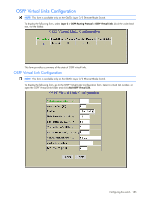
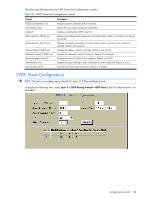
OSPF Area Configuration NOTE: This form is available only on the GbE2c Layer 2/3 Ethernet Blade Switch. To display the following form, go to the OSPF Areas Configuration form. Select an area number, or open the OSPF Areas folder and click Add OSPF Area. The following table describes the OSPF Area Configuration controls: Table 147 OSPF Area Configuration controls Control Descriptions Area number (0-2) Area ID Enabled? Area Type Stub Area Metric (1-65535) SPF Interval (0-255) Authentication Type? Assigns a numeric identifier for the OSPF area. Defines the area ID of the OSPF area number. Enables or disables the OSPF area. Defines the type of area. For example, when a virtual link has to be established with the backbone, the area type must be defined as transit. • Transit area: allows area summary information to be exchanged between routing devices. Any area that is not a stub area or NSSA is considered to be transit area. • Stub area: is an area where external routing information is not distributed. Typically, a stub area is connected to only one other area. • NSSA: Not-So-Stubby Area (NSSA) is similar to stub area with additional capabilities. For example, routes originating from within the NSSA can be propagated to adjacent transit and backbone areas. External routes from outside the Autonomous System (AS) can be advertised within the NSSA but are not distributed into other areas. Configures a stub area to send a numeric metric value. All routes received via that stub area carry the configured metric to potentially influencing routing decisions. Metric value assigns the priority for choosing the switch for default route. Metric type determines the method for influencing routing decisions for external routes. Sets time interval between two successive SPF (shortest path first) calculations of the shortest path tree using the Dijkstra's algorithm. Defines the authentication method, as follows: • None: No authentication required. • Password: Authenticates simple passwords so that only trusted routing devices can participate. • MD5: This parameter is used when MD5 cryptographic authentication is required. Configuring the switch 179