Ricoh Priport HQ7000 Network Guide - Page 119
The IEEE 802.11b I/F MAC address is dis, IEEE 802.11b TX Rate <Transfer Speed>
 |
View all Ricoh Priport HQ7000 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 119 highlights
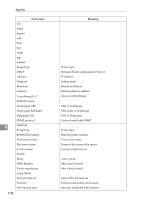
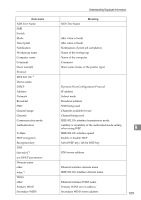
Message List Message Causes and solutions IEEE 802.11b mode Transmission mode for IEEE 802.11b (Example: current mode is infrastructure mode.) IEEE 802.11b [infrastructure] mode (Example: current mode is 802.11 ad hoc mode.) IEEE 802.11b [802.11 ad hoc] mode (Example: current mode is ad hoc mode.) IEEE 802.11b [ad hoc] mode IEEE 802.11b current channel The current channel is displayed. The value selected by the user is displayed in ad hoc mode. The channel used in the access point is displayed in infrastructure mode. (Example: current channel is 11.) IEEE 802.11b current channel 11 IEEE 802.11b Card Firmware REV. IEEE 802.11b interface unit Firmware version (Example: current version is 0.8.3.) IEEE 802.11b interface unit Firmware REV. 0.8.3 IEEE 802.11b MAC Address = The IEEE 802.11b I/F MAC address is displayed. (Example: current MAC address is 00:00:74:XX:XX:XX.) IEEE 802.11b MAC Address = 00:00:74:XX:XX:XX IEEE 802.11b SSID (AP MAC Address < MAC Address>) The access point SSID used in infrastructure mode and the MAC address of the access point are displayed. (Example: current MAC address is xx:xx:xx:xx:xx:xx and SSID value is "testssid".) IEEE 802.11b SSID test-ssid (AP MAC Address xx:xx:xx:xx:xx:xx) IEEE 802.11b TX Rate The IEEE 802.11b transmitting speed (set speed) is displayed. (Example: current Tx Rate is 11 Mbps.) IEEE 802.11b Tx Rate 11 Mbps Transmission speeds vary depending on signal quality. Displayed values may differ from actual transmission speed. inetd start. An inetd has started. started with IP: has been set for and started. 9 113