Cisco E4200 User Guide - Page 41
Applications and Gaming > QoS, WMM Support, No Acknowledgement, Enabled/Disabled, Upstream Bandwidth - router connection issues
 |
View all Cisco E4200 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 41 highlights
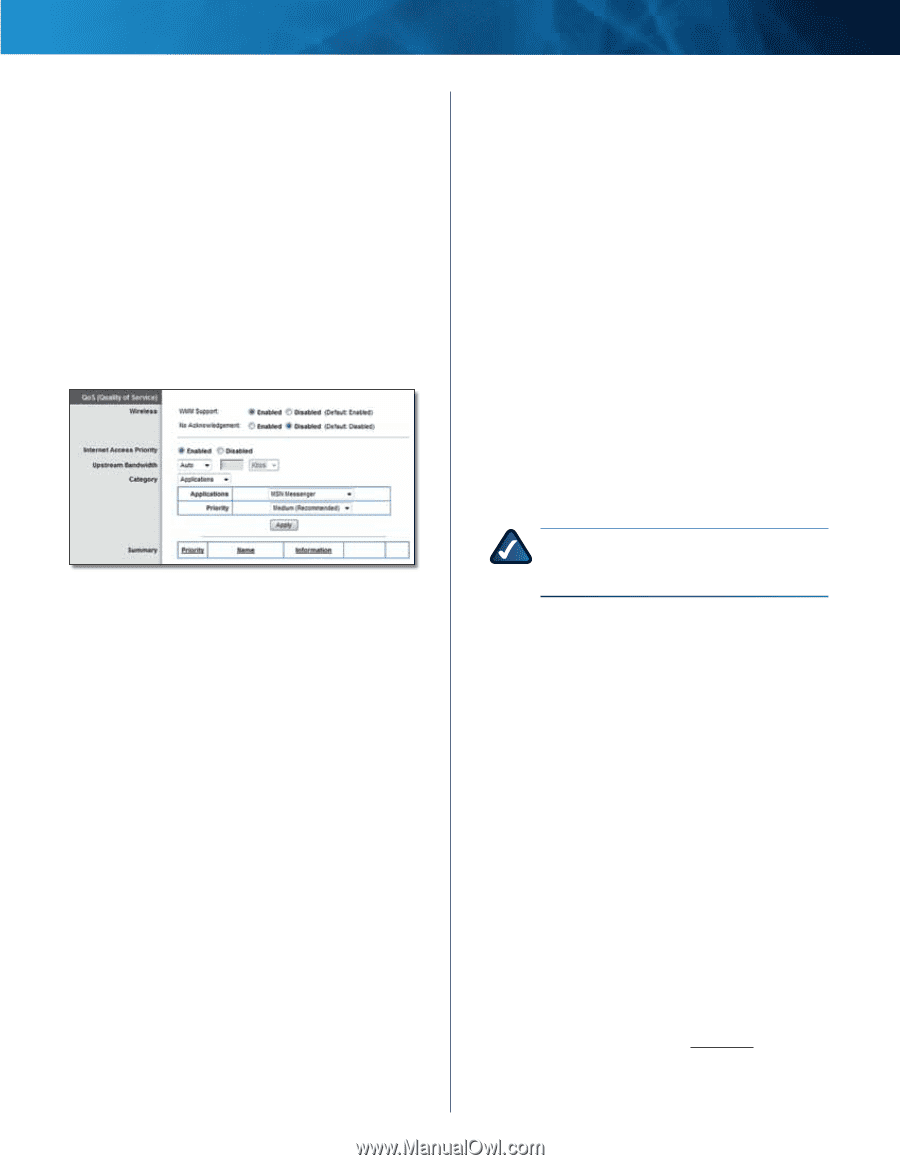
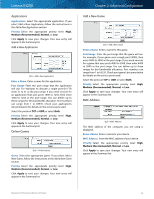
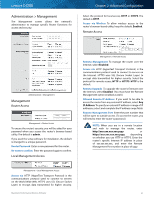
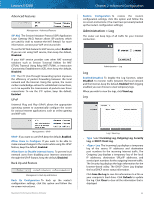
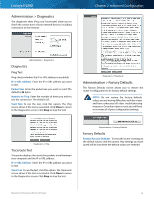
Linksys E4200 To select a DHCP client, click Select. To update the onscreen information, click Refresh. To exit this screen and return to the DMZ screen, click Close. Applications and Gaming > QoS Quality of Service (QoS) is a method that assigns priority to specific types of network traffic, which often are demanding, real-time applications, such as online gaming, VoIP calls, video streaming, and videoconferencing. QoS can mark packets to designate different levels of priority, so it helps to ensure optimal performance for the most important, real-time applications. QoS is only applied to traffic streams that are uploaded to the Internet. QoS cannot be guaranteed after the traffic streams reach the Internet. Applications and Gaming > QoS QoS (Quality of Service) Wireless WMM Support The Wi-Fi MultiMedia (WMM) feature is a wireless QoS feature based on the IEEE 802.11e standard. WMM improves quality for audio, video, and voice applications by prioritizing wireless traffic. To use this feature, the wireless client devices in your network must support WMM. To disable this option, select Disabled. Otherwise, keep the default, Enabled. No Acknowledgement If you want the router to re-send data if an error occurs, keep the default, Disabled. If you do not want the router to re-send data if an error occurs, select Enabled. Internet Access Priority The router is the interface between the local network and the Internet. The user can configure the router to assign higher priority for these categories: Applications, Online Games, MAC Address, and Voice Device. In this section, you can set the bandwidth priority for a variety of applications and devices. There are four levels of priority: High, Medium, Normal, or Low. When you set priority, do not set all applications to High, because this will defeat the purpose of allocating the available bandwidth. If you want to select below-normal bandwidth, select Maximum Performance Wireless-N Router Chapter 2: Advanced Configuration Low. Depending on the application, a few attempts may be needed to set the appropriate bandwidth priority. Enabled/Disabled To use the QoS policies you set, select Enabled. Otherwise, keep the default, Disabled. Upstream Bandwidth The Upstream Bandwidth feature sets the maximum outgoing bandwidth that applications can use. The default, Auto, allows the router to set the maximum. The router sets speeds that are multiples of 512 Kbps. Here are a couple of examples: •• If the router auto-detects an upstream speed between 512 Kbps and 1024 Kbps, it will set the maximum at 512 Kbps. •• If the router auto-detects an upstream speed of 2300 Kbps, it will set the maximum at 2048 Kbps (512 Kbps x 4). Upstream Bandwidth This option sets the maximum outgoing bandwidth of your Internet connection. To allow the router to detect the maximum, keep the default, Auto. To specify the maximum, select Manual. Then enter the appropriate bandwidth and select Kbps or Mbps. NOTE: If the maximum bandwidth is too high, then the router cannot apply QoS properly, and there will be adverse QoS issues. Category You can define the Internet access priority level for as many selections as you want. The Summary section will display all of the priority selections that you enter. Select from the following categories: •• Applications Allows you to assign a priority level for a predefined application or one that you add. •• Online Games Allows you to assign a priority level for a preset game or one that you add. •• MAC Address This option lets you prioritize network traffic based on the device that is accessing the network. For example, if you want your gaming console to have higher priority accessing the Internet than your computer, you can assign their priority levels using their respective MAC addresses. •• Voice Device Voice devices require a higher priority level. You can assign a higher priority level to voice devices using their respective MAC addresses. Summary This lists the QoS entries you have created for your applications and devices. Go to "Summary" on page 40 for more information. 38