D-Link DES-3028 Product Manual - Page 117
Router Ports Settings, L2 Features, IGMP Snooping > Router Ports Settings, Modify
 |
UPC - 790069305375
View all D-Link DES-3028 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 117 highlights
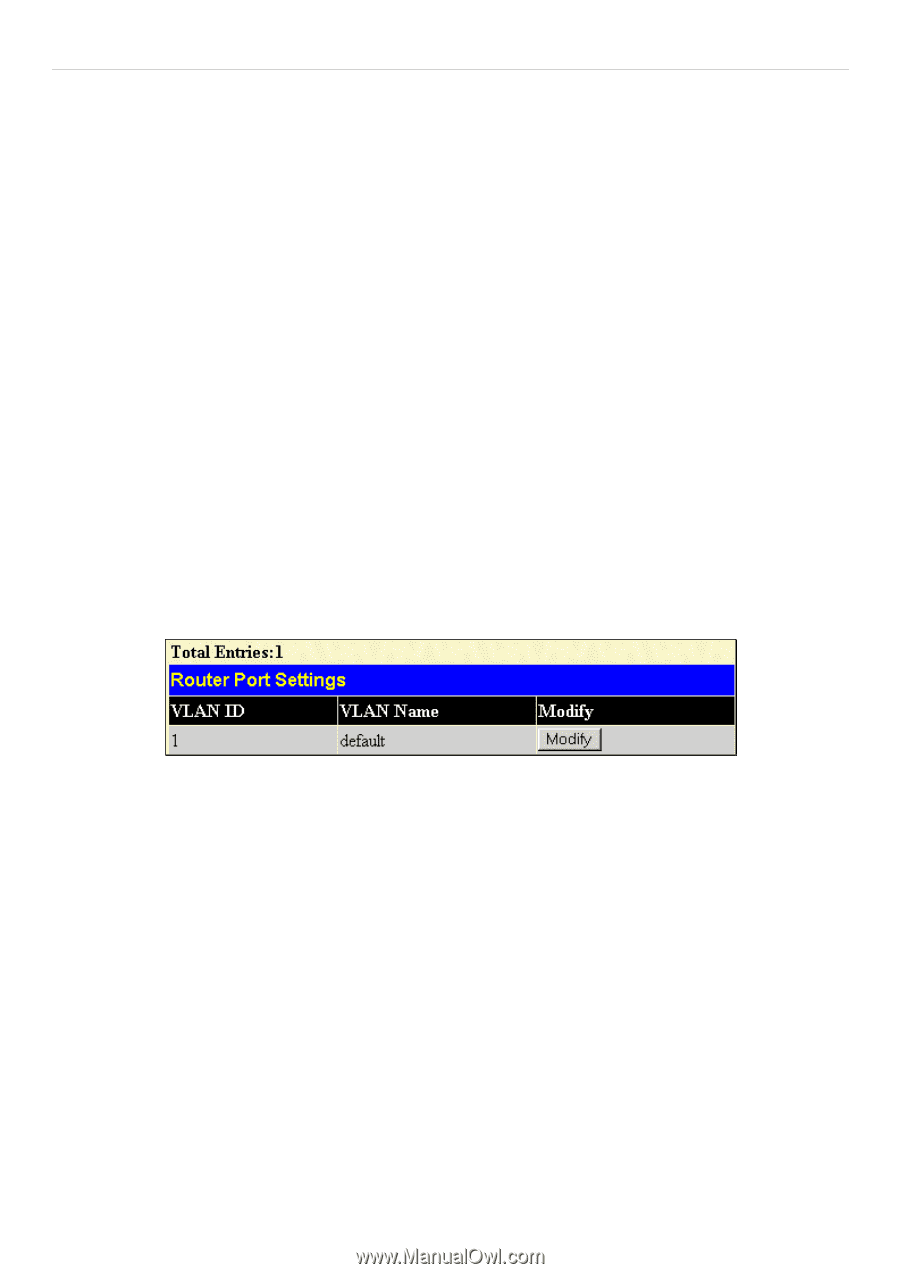
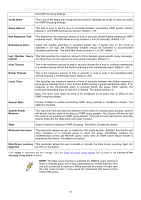
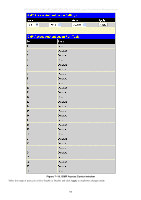
DES-3028 DES-3028P DES-3028G DES-3052 DES-3052P Layer 2 Fast Ethernet Managed Switch Router Ports Settings A static router port is a port that has a multicast router attached to it. Generally, this router would have a connection to a WAN or to the Internet. Establishing a router port will allow multicast packets coming from the router to be propagated through the network, as well as allowing multicast messages (IGMP) coming from the network to be propagated to the router. A router port has the following behavior: All IGMP Report packets will be forwarded to the router port. IGMP queries (from the router port) will be flooded to all ports. All UDP multicast packets will be forwarded to the router port. Because routers do not send IGMP reports or implement IGMP snooping, a multicast router connected to the router port of a Layer 3 switch would not be able to receive UDP data streams unless the UDP multicast packets were all forwarded to the router port. A router port will be dynamically configured when IGMP query packets, RIPv2 multicast, DVMRP multicast or PIM-DM multicast packets are detected flowing into a port. IGMP query packets - Internet Group Management Protocol query packets work by controlling the flow of multicast traffic. The IGMP query packets works by sending messages out to determine which devices are members of a particular multicast group, the devices will respond to the query and inform the querier of its membership status. RIPv2 multicast- Routing Information Protocol Version 2 can be used for small networks or on the perifory of larger networks where VLSM is required. RIPv2 is used to support route authentication and multicasting of route updates. RIPv2 sends updates every 30 seconds and it uses triggered updates to carry out loop-prevention and poison reverse or counting to infinity. DVMRP multicast - Distance Vector Multicast Routing Protocol uses reverse path flooding. Messages are flooded out of all interfaces except the one that returns to the souce, this is to prevent any packets traveling to members of the multicast VLAN. The DVMRP uses periodic flooding so as to establish if there are other or potentially new group members. PIM-DM multicast- Protocol Independent Multicast Dense Mode works by flooding the multicast packets to all routers and eliminates groups or members of groups that don't have an efficient path or route to their members. This mode is generally used if the volume of multicast traffic is large and constant. To view this window click L2 Features > IGMP Snooping > Router Ports Settings. Figure 7- 17. Router Ports Settings window The Router Ports Settings page (shown above) displays all the current entries on the Switch's static router port table. To modify an entry, click the Modify button. This will open the following window: 103