D-Link DES-3028 Product Manual - Page 217
Guest VLANs, Vendor-Specific attribute, Description, Value, Usage
 |
UPC - 790069305375
View all D-Link DES-3028 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 217 highlights
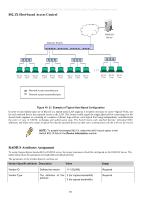
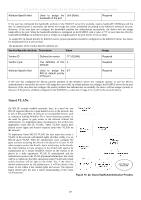
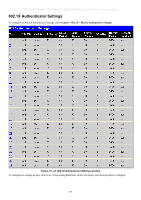
DES-3028 DES-3028P DES-3028G DES-3052 DES-3052P Layer 2 Fast Ethernet Managed Switch Attribute-Specific field Used to assign the Unit (Kbits) bandwidth of the port Required If the user has configured the bandwidth attribute of the RADIUS server (for example, ingress bandwidth 1000Kbps) and the 802.1X authentication is successful, the device will assign the correct bandwidth (according to the RADIUS server) to the port. However, if the user does not configure the bandwidth attribute but authenticates successfully, the device will not assign bandwidth to the port. When the bandwidth attribute is configured on the RADIUS with a value of "0" or more than the effective bandwidth (100Mbps on an Ethernet port or 1Gbps on a Gigabit port) of the port will be set to no_limit. To assign 802.1p default priority by RADIUS server, proper parameters should be configured on the RADIUS Server. See below for the parameters of a user account. The parameters of the Vendor-Specific attribute are: Vendor-Specific attribute Description Value Usage Vendor-ID Vendor-Type Attribute-Specific field Defines the vendor 171 (DLINK) The definition of this 4 attribute Used to assign the 0-7 802.1p default priority of the port Required Required Required If the user has configured the 802.1p priority attribute of the RADIUS server (for example, priority 7) and the 802.1X authentication is successful, the device will assign the correct 802.1p default priority (according to the RADIUS server) to the port. However, if the user does not configure the priority attribute but authenticates successfully, the device will not assign a priority to this port. If the priority attribute configured on the RADIUS is a value out of range (>7), it will not be set to the device. Guest VLANs On 802.1X security enabled networks, there is a need for non 802.1X supported devices to gain limited access to the network, due to lack of the proper 802.1X software or incompatible devices, such as computers running Windows 98 or lower operating systems, or the need for guests to gain access to the network without full authorization. To supplement these circumstances, this switch now implements Guest 802.1X VLANs. These VLANs should have limited access rights and features separate from other VLANs on the network. To implement Guest 802.1X VLAN, the user must first create a VLAN on the network with limited rights and then enable it as an 802.1X guest VLAN. Then the administrator must configure the guest accounts accessing the Switch to be placed in a Guest VLAN when trying to access the Switch. Upon initial entry to the Switch, the client wishing to have services on the Switch will need to be authenticated by a remote RADIUS Server on the Switch to be placed in a fully operational VLAN. If authenticated and the authenticator posseses the VLAN placement information, that client will be accepted into the fully operational target VLAN and normal switch functions will be open to the client. Yet, if the client is denied authentication by the authenticator, it will be placed in the Guest VLAN where it has limited rights and access. The adjacent figure should give the user a better understanding of the Guest VLAN process. Client Placed in Guest VLAN Figure 10- 22. Guest VLAN Authentication Process 203