HP 6125G HP 6125G & 6125G/XG Blade Switches Layer 3 - IP Routing Confi - Page 143
Specifying the source interface for TCP connections
 |
View all HP 6125G manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 143 highlights
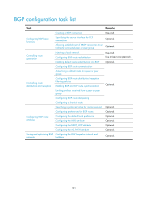
Step Command Remarks 1. Enter system view. system-view N/A 2. Configure a global router ID. router id router-id 3. Enable BGP and enter BGP view. bgp as-number Optional. Not configured by default. If no global router ID is configured, the highest loopback interface IP address-if any-is used as the router ID. If no loopback interface IP address is available, the highest physical interface IP address is used, regardless of the interface status. Not enabled by default. 4. Specify a router ID. router-id router-id Optional. By default, the global router ID is used. 5. Specify a peer or a peer group and its AS number. peer { group-name | ip-address } as-number as-number Not specified by default. 6. Enable the default use of IPv4 unicast address family for the peers that are established default ipv4-unicast using the peer as-number command. Optional. Enabled by default. 7. Enable a peer. peer ip-address enable Optional. Enabled by default. A router can reside in only one AS, so the router can run only one BGP process. Not configured by default. 8. Configure a description for a peer { group-name | ip-address } peer/peer group. description description-text You must create a peer group before configuring it. Specifying the source interface for TCP connections BGP uses TCP as the transport layer protocol. By default, BGP uses the output interface of the optimal route to a peer/peer group as the source interface for establishing TCP connections to the peer or peer group. If a BGP router has multiple links to a peer, and the source interface fails, BGP must reestablish TCP connections, causing network oscillation. To enhance stability of BGP connections, HP recommends using a loopback interface as the source interface. To establish multiple BGP connections between two routers, you must specify the source interface for establishing TCP connections to each peer on the local router; otherwise, the local BGP router may fail to establish TCP connections to a peer when using the outbound interface of the best route to the peer as the source interface. To specify the source interface for TCP connections: 133