HP 6125G HP 6125G & 6125G/XG Blade Switches Layer 3 - IP Routing Confi - Page 287
Configuring OSPF between MCE and VPN site, Con the MCE
 |
View all HP 6125G manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 287 highlights
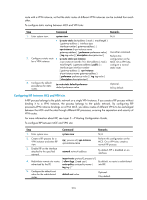
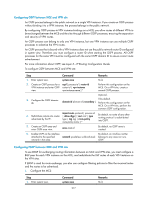
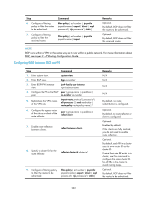
Configuring OSPF between MCE and VPN site An OSPF process belongs to the public network or a single VPN instance. If you create an OSPF process without binding it to a VPN instance, the process belongs to the public network. By configuring OSPF process-to-VPN instance bindings on a MCE, you allow routes of different VPNs to be exchanged between the MCE and the sites through different OSPF processes, ensuring the separation and security of VPN routes. An OSPF process can belong to only one VPN instance, but one VPN instance can use multiple OSPF processes to advertise the VPN routes. An OSPF process that is bound with a VPN instance does not use the public network router ID configured in system view. Therefore, you must configure a router ID when starting the OSPF process. All OSPF processes for the same VPN must be configured with the same OSPF domain ID to ensure correct route advertisement. For more information about OSPF, see Layer 3-IP Routing Configuration Guide. To configure OSPF between MCE and VPN site: Step Command Remarks 1. Enter system view. system-view N/A 2. Create an OSPF process for a ospf [ process-id | router-id VPN instance and enter OSPF router-id | vpn-instance view. vpn-instance-name ] * Perform this configuration on the MCE. On a VPN site, create a normal OSPF process. 3. Configure the OSPF domain ID. domain-id domain-id [ secondary ] Optional. 0 by default. Perform this configuration on the MCE. On a VPN site, perform the common OSPF configuration. import-route protocol [ process-id 4. Redistribute remote site routes | allow-ibgp ] [ cost cost | type advertised by the PE. type | tag tag | route-policy route-policy-name ] * By default, no route of any other routing protocol is redistributed into OSPF. 5. Create an OSPF area and enter OSPF area view. area area-id By default, no OSPF area is created. 6. Enable OSPF on the interface By default, an interface neither attached to the specified network ip-address wildcard-mask belongs to any area nor runs network in the area. OSPF. Configuring EBGP between MCE and VPN site To use EBGP for exchanging routing information between an MCE and VPN sites, you must configure a BGP peer for each VPN instance on the MCE, and redistribute the IGP routes of each VPN instance on the VPN sites. If EBGP is used for route exchange, you also can configure filtering policies to filter the received routes and the routes to be advertised. 1. Configure the MCE: Step 1. Enter system view. Command system-view 277 Remarks N/A