HP 6125G HP 6125G & 6125G/XG Blade Switches Layer 3 - IP Routing Confi - Page 165
Configuring BGP community, Configuring a BGP route reflector
 |
View all HP 6125G manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 165 highlights
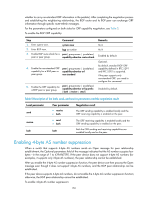
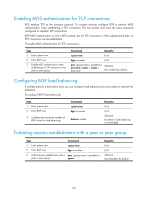
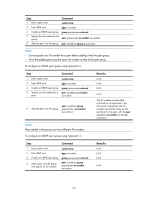
NOTE: • Do not specify any AS number for a peer before adding it into the peer group. • Peers added in the group can have different AS numbers. Configuring BGP community A BGP community is a group of destinations with the same characteristics. It has no geographical boundaries and is independent of ASs. You can configure a routing policy to define which destinations belong to a BGP community and then advertise the COMMUNITY attribute to a peer or peer group. You can apply a routing policy to filter routes advertised to or received from a peer or peer group according to the COMMUNITY attribute, which helps simplify policy configuration and management. For how to configure a routing policy, see "Configuring routing policies." To configure BGP community: Step 1. Enter system view. 2. Enter BGP view. 3. Advertise the COMMUNITY attribute to a peer or peer group. 4. Apply a routing policy to routes advertised to a peer or peer group. Command system-view bgp as-number • Advertise the COMMUNITY attribute to a peer or peer group: peer { group-name | ip-address } advertise-community • Advertise the extended community attribute to a peer or peer group: peer { group-name | ip-address } advertise-ext-community peer { group-name | ip-address } route-policy route-policy-name export Remarks N/A N/A Not configured by default. Not configured by default. Configuring a BGP route reflector If an AS has many BGP routers, you can configure them as a cluster by configuring one of them as a route reflector and others as clients to reduce IBGP connections. To enhance network reliability and prevent single point of failure, specify multiple route reflectors for a cluster. The route reflectors in the cluster must have the same cluster ID to avoid routing loops. It is not required to make clients of a route reflector fully meshed. The route reflector forwards routing information between clients. If clients are fully meshed, disable route reflection between clients to reduce routing costs. Generally, a cluster has only one route reflector, and the router ID is used to identify the cluster. You can configure multiple route reflectors to improve network stability. To avoid routing loops, specify the same cluster ID for these route reflectors by using the reflector cluster-id command. To configure a BGP route reflector: 155