HP 6125G HP 6125G & 6125G/XG Blade Switches Layer 3 - IP Routing Confi - Page 254
Configuring a large-scale IPv6 BGP network, Configuration prerequisites
 |
View all HP 6125G manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 254 highlights
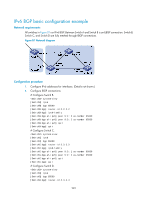
Step Command Remarks 2. Enter BGP view. bgp as-number N/A 3. Enter IPv6 address family view. ipv6-family N/A 4. Enable MD5 authentication when establishing a TCP peer { ipv6-group-name | connection to the peer or peer ipv6-address } password { cipher | Not enabled by default. group. simple } password Configuring a large-scale IPv6 BGP network In a large-scale IPv6 BGP network, configuration and maintenance become inconvenient because of too many peers. Configuring peer groups makes management easier and improves route distribution efficiency. Peer group includes IBGP peer group, where peers belong to the same AS, and EBGP peer group, where peers belong to different ASs. If peers in an EBGP group belong to the same external AS, the EBGP peer group is a pure EBGP peer group, and if not, a mixed EBGP peer group. In a peer group, all members have a common policy. Using the COMMUNITY attribute can make a set of IPv6 BGP routers in multiple ASs have the same policy because community sending between IPv6 BGP peers is not limited by AS. To assure connectivity between IBGP peers, make them fully meshed, but it becomes impractical when too many IBGP peers exist. Using route reflectors or confederation can solve this issue. In a large-scale AS, both of them can be used. Confederation configuration of IPv6 BGP is identical to that of BGP4, so it is not mentioned here. Configuration prerequisites Before you configure a large-scale IPv6 BGP network, complete the following tasks: • Make peer nodes accessible to each other at the network layer. • Enable BGP and configure a router ID. Configuring IPv6 BGP peer group Configuring an IBGP peer group Step 1. Enter system view. 2. Enter BGP view. 3. Enter IPv6 address family view. 4. Create an IBGP peer group. 5. Add a peer into the group. Command system-view bgp as-number Remarks N/A N/A ipv6-family N/A group ipv6-group-name [ internal ] N/A peer ipv6-address group ipv6-group-name [ as-number as-number ] Not added by default. 244