HP 6125G HP 6125G & 6125G/XG Blade Switches Layer 3 - IP Routing Confi - Page 163
Configuring a large scale BGP network, Configuration prerequisites, Configuring BGP peer groups
 |
View all HP 6125G manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 163 highlights
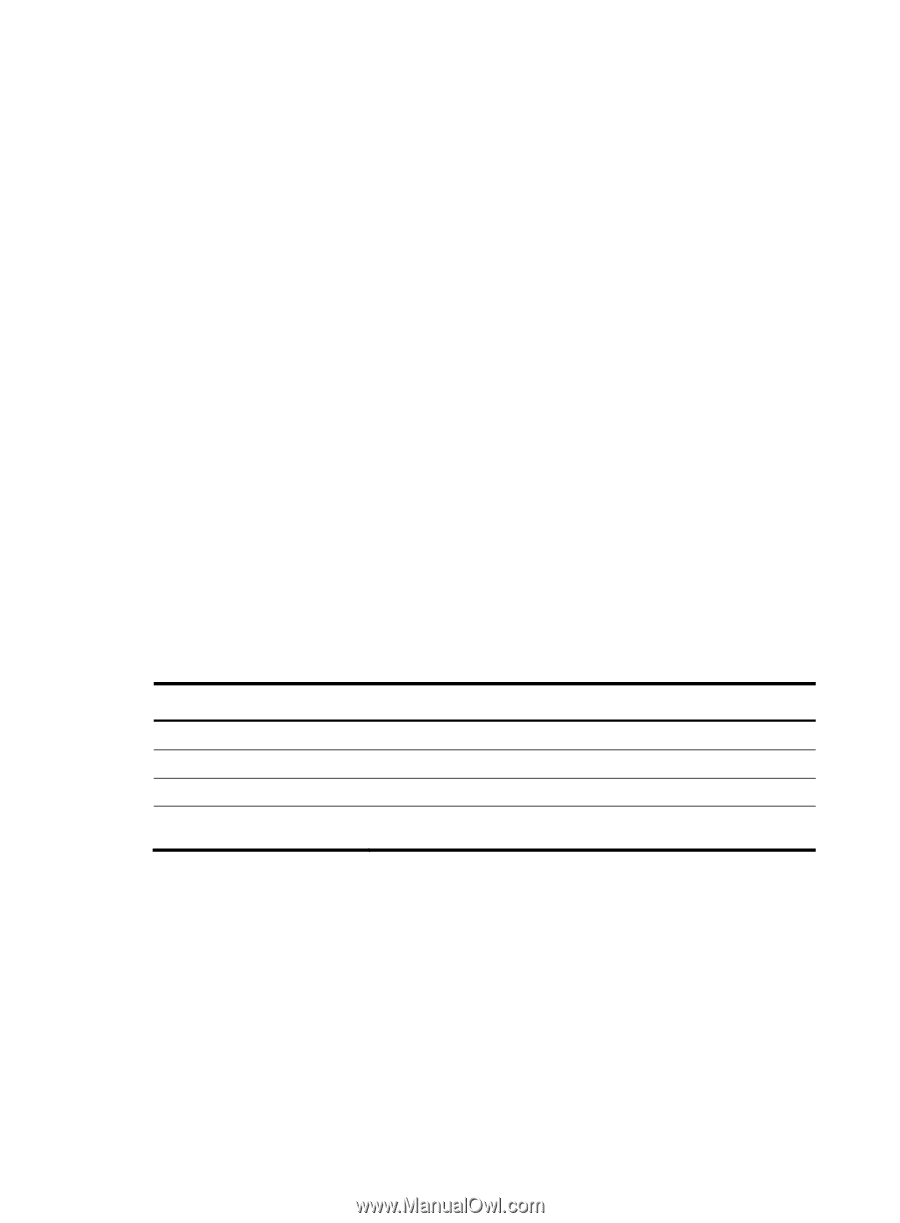
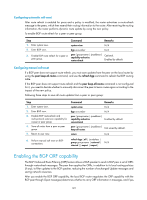
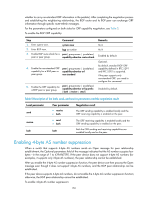
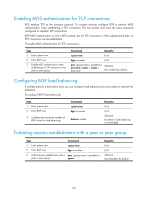
Configuring a large scale BGP network In a large-scale BGP network, configuration and maintenance become difficult because of the large numbers of BGP peers. To facilitate configuration, you can configure peer group, community, route reflector, or confederation as needed. Configuration prerequisites Peering nodes are accessible to each other at the network layer. Configuring BGP peer groups A peer group is a group of peers with the same route selection policy. In a large-scale network, many peers may use the same route selection policy. You can configure a peer group and add these peers into this group. In this way, peers can share the same policy as the peer group. When the policy of the group is modified, the modification also applies to peers in it, simplifying configuration. A peer group is an IBGP peer group if peers in it belong to the same AS, and is an EBGP peer group if peers in it belong to different ASs. If a peer group has peers added, you cannot remove its AS number using the undo form of the command or change its AS number. Configuring an IBGP peer group After you create an IBGP peer group and then add a peer into it, the system creates the peer in BGP view and specifies the local AS number for the peer. To configure an IBGP peer group: Step 1. Enter system view. 2. Enter BGP view. 3. Create an IBGP peer group. 4. Add a peer into the IBGP peer group. Command system-view bgp as-number group group-name [ internal ] peer ip-address group group-name Configuring an EBGP peer group If peers in an EBGP group belong to the same external AS, the EBGP peer group is a pure EBGP peer group; if not, it is a mixed EBGP peer group. Use one of the following approaches to configure an EBGP peer group: • Create the EBGP peer group, specify its AS number, and add peers into it. All the added peers share the same AS number. • Create the EBGP peer group, specify an AS number for a peer, and add the peer into the peer group. • Create the EBGP peer group and add a peer into it with an AS number specified. To configure an EBGP peer group using Approach 1: 153