HP 6125G HP 6125G & 6125G/XG Blade Switches Layer 3 - IP Routing Confi - Page 249
Tuning and optimizing IPv6 BGP networks
 |
View all HP 6125G manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 249 highlights
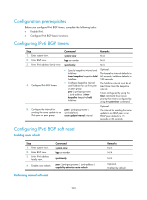
Step 1. Enter system view. 2. Enter BGP view. 3. Enter IPv6 address family view. 4. Allow the local AS number to appear in AS_PATH of routes from a peer or peer group and specify the repeat times. Command system-view bgp as-number ipv6-family peer { ipv6-group-name | ipv6-address } allow-as-loop [ number ] 5. Specify a fake AS number for peer { ipv6-group-name | an IPv6 peer or peer group. ipv6-address } fake-as as-number 6. Disable IPv6 BGP from considering the AS_PATH during best route selection. bestroute as-path-neglect 7. Configure to carry only the public AS number in updates peer { ipv6-group-name | sent to a peer or peer group. ipv6-address } public-as-only 8. Substitute the local AS number for the AS number of an IPv6 peer { ipv6-group-name | peer or peer group identified ipv6-address } substitute-as in the AS_PATH attribute. Remarks N/A N/A N/A Optional. Not allowed by default. Optional. Not specified by default. Optional. Enabled by default. Optional. By default, IPv6 BGP updates carry a private AS number. Optional. Not substituted by default. Tuning and optimizing IPv6 BGP networks This section describes configurations of IPv6 BGP timers, IPv6 BGP connection soft reset, and the maximum number of load balanced routes. • IPv6 BGP timers After establishing an IPv6 BGP connection, two routers send keepalive messages periodically to each other to maintain the connection. If a router receives no keepalive message from the peer after the holdtime elapses, it tears down the connection. When establishing an IPv6 BGP connection, the two parties compare their holdtimes, taking the shorter one as the common holdtime. If the holdtime is 0, neither keepalive massage is sent, nor holdtime is checked. • IPv6 BGP connection soft reset After modifying a route selection policy, you must reset IPv6 BGP connections to make the new one take effect. The current IPv6 BGP implementation supports the route-refresh feature that enables dynamic route refresh without needing to disconnect IPv6 BGP links. After this feature is enabled on all IPv6 BGP routers, a router that wants to apply a new route selection policy advertises a route-refresh message to its peers, which then send their routing information to the router. After receiving the routing information, the router can perform dynamic route update by using the new policy without tearing down connections. If a peer not supporting route-refresh exists in the network, you must configure the peer keep-all-routes command to save all routes from the peer. When the routing policy is changed, the system will update the IPv6 BGP routing table and apply the new policy. 239