Cisco 7920 Administration Guide - Page 42
Interacting with the Cisco Aironet Access Point - web protection
 |
UPC - 746320774732
View all Cisco 7920 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 42 highlights
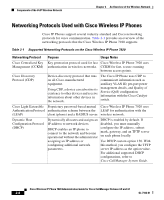
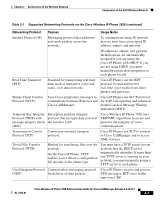
Components of the VoIP Wireless Network Chapter 2 An Overview of the Wireless Network Table 2-1 Supported Networking Protocols on the Cisco Wireless IP Phone 7920 (continued) Networking Protocol Wi-Fi (802.11b) Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP) Wireless Protected Access (WPA) Purpose An open standard that defines wireless methods of transmitting Ethernet traffic and is commonly called Wi-Fi. This standard defines radio frequencies (RF) and data speed for wireless LAN communications. Wireless security protocol for encrypting data that uses an encryption key stored on the phone and access point. Provides stronger authentication, encryption key management and alternative encryption and message integrity methods. Usage Notes Cisco Wireless IP Phone 7920 uses the 802.11b standard with a range of 2.4-2.497 GHz RF and dynamic data rate scaling of 1, 2, 5.5, and 11 Mbps. Cisco Wireless IP Phone 7920 can use either static WEP or dynamic WEP keys for encryption, depending on the network security configuration. Cisco Wireless IP Phone 7920 supports both WPA and WPA Pre-shared key authentication, including encryption using TKIP and MIC (message integrity check) Related Topics • Understanding the Phone Startup Process, page 2-21 • Components of the VoIP Wireless Network, page 2-5 • Modifying DHCP Settings, page 5-4 • Configuring TFTP Option, page 5-9 Interacting with the Cisco Aironet Access Point Wireless voice devices use the same access points as wireless data devices. However, voice traffic over a WLAN requires different equipment configurations and layouts than a WLAN that is used exclusively for data traffic. Data transmission can tolerate a higher level of RF noise, packet loss, and channel contention than voice transmission. Packet loss while searching a web page might Cisco Wireless IP Phone 7920 Administration Guide for Cisco CallManager Release 4.0 and 4.1 2-8 OL-7104-01