Cisco 7920 Administration Guide - Page 44
Roaming in a Wireless Network, Securing Voice Communications - utility
 |
UPC - 746320774732
View all Cisco 7920 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 44 highlights
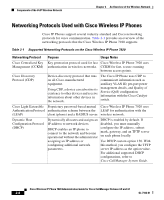
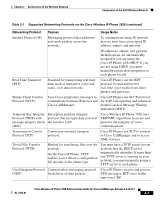
Components of the VoIP Wireless Network Chapter 2 An Overview of the Wireless Network • QoS Basis Service Set (QBSS)-The access point uses this beacon information element (IE) to send the channel utilization of the access point to the Cisco Wireless IP Phone. The phone uses the QBSS value to determine whether the access point can effectively handle more traffic. The Cisco Wireless IP Phone associates with the access point with the highest RSSI and lowest channel utilization values (QBSS) that have matching SSID and encryption types. Related Topics • Roaming in a Wireless Network, page 2-10 • Securing Voice Communications, page 2-4 • Wireless Network and Access Point Configuration, page 2-19 Roaming in a Wireless Network Cisco Wireless IP Phone users have the ability to move from one location in the premises to another while conversing on the phone. Unlike cellular phones that have broad coverage, the coverage area for the Cisco Wireless IP Phone is smaller; therefore, phone users must roam from one access point to another more frequently. To understand some of the limitations of roaming with wireless IP phones, the following examples provide information about roaming in the WLAN. • Pre-call Roaming-A Cisco Wireless IP Phone 7920 user powers on the phone in the office, and the phone associates with the nearby access point. The user leaves the building and moves to another building where he places a call. The phone associates with a different access point in order to place the call from the new location. If the associated access point is within the same Layer 2 VLAN, the IP address remains the same for the phone. But, if the roaming phone crosses a Layer 3 boundary with DHCP enabled, the phone recognizes that it is no longer in the same subnet. The phone requests a new IP address before it can connect to the network and place the call. • Mid-call Roaming-A Cisco Wireless IP Phone 7920 user is actively engaged in a call and moves from one building to another. The roaming event occurs when the phone moves into the range of a different access point, and the phone authenticates and associates with the new access point. The current access point hands the call over to the new access point while maintaining continuous audio connection without user intervention. As long as the access 2-10 Cisco Wireless IP Phone 7920 Administration Guide for Cisco CallManager Release 4.0 and 4.1 OL-7104-01