Cisco ACE-4710-K9 Administration Guide - Page 257
Stateful Failover - end of support
 |
View all Cisco ACE-4710-K9 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 257 highlights
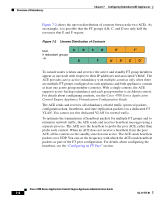
Chapter 7 Configuring Redundant ACE Appliances Overview of Redundancy The election of the active member within each FT group is based on a priority scheme. The member configured with the higher priority is elected as the active member. If a member with a higher priority is found after the other member becomes active, the new member becomes active because it has a higher priority. This behavior is known as preemption and is enabled by default. You can override this default behavior by disabling preemption. To disable preemption, use the preempt command. Entering this command causes the member with the higher priority always to assert itself and become active. See the "Configuring an FT Group" section. Stateful Failover The ACE replicates flows on the active FT group member to the standby group member per connection for each context. The replicated flows contain all the flow-state information necessary for the standby member to take over the flow if the active member becomes unresponsive. If the active member becomes unresponsive, the replicated flows on the standby member become active when the standby member assumes mastership of the context. The active flows on the former active member transition to a standby state to fully back up the active flows on the new active member. Note By default, connection replication is enabled in the ACE. After a switchover occurs, the same connection information is available on the new active member. Supported end-user applications do not need to reconnect to maintain the same network session. Note The ACE does not replicate SSL and other terminated (proxied) connections from the active context to the standby context. The state information passed to the standby appliance includes the following data: • Network Address Translation (NAT) table based on information synchronized with the connection record • All Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) and User Datagram Protocol (UDP) connections not terminated by the ACE OL-11157-01 Cisco 4700 Series Application Control Engine Appliance Administration Guide 7-5