DES-3010F / DES-3010G / DES-3018 / DES-3026 Layer 2 Switch CLI Reference Manual
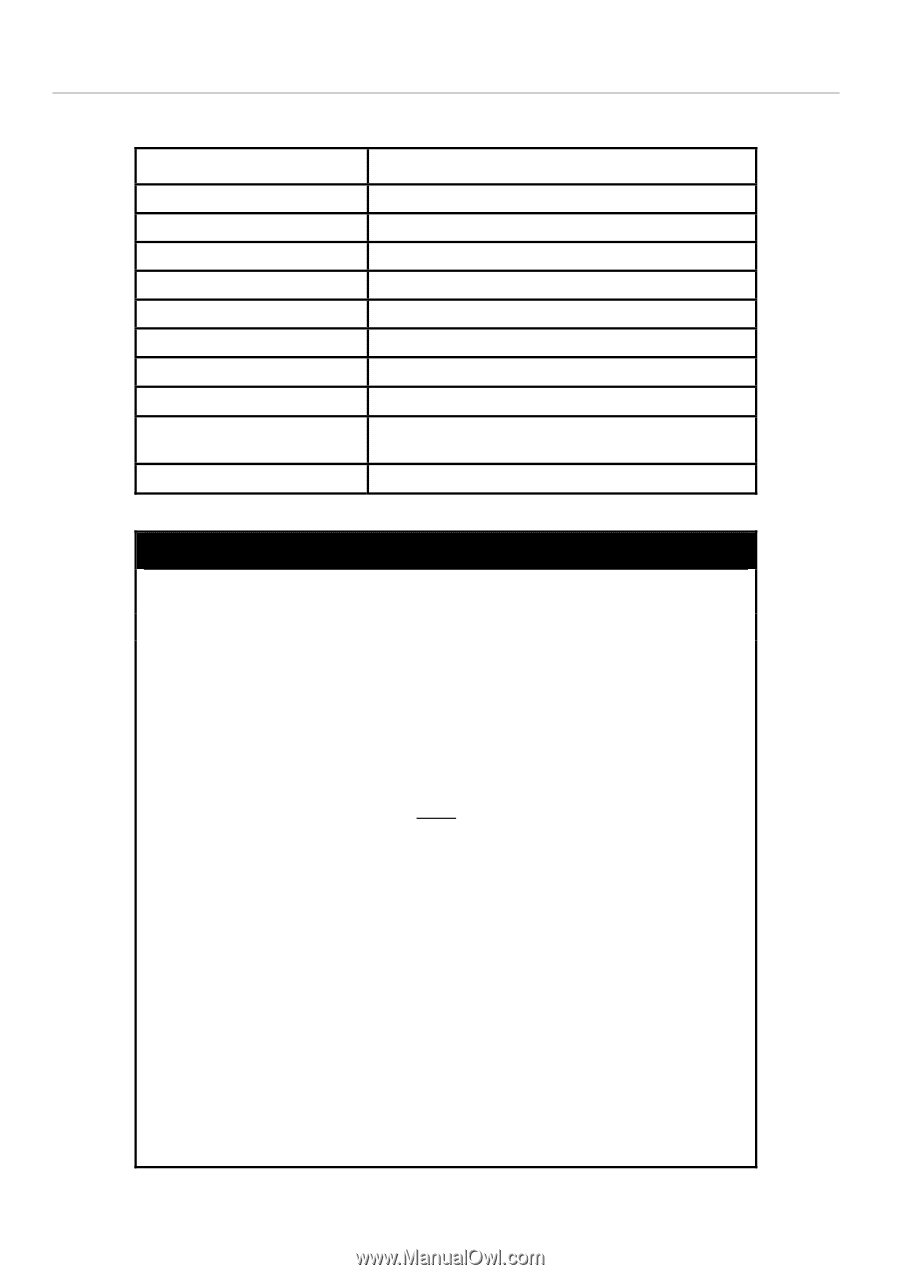
The QoS commands in the Command Line Interface (CLI) are listed (along with the appropriate parameters) in the following
table.
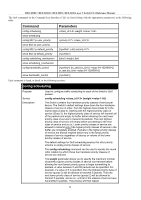
Command
Parameters
config scheduling
<class_id 0-3> weight <value 1-55>
show scheduling
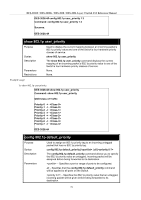
config 802.1p user_priority
<priority 0-7> <class_id 0-3>
show 802.1p user_priority
config 802.1p default_priority
[<portlist> | all] <priority 0-7>
show 802.1p default_priority
{<portlist>}
config scheduling_mechanism
[strict | weight_fair]
show scheduling_mechanism
config bandwidth_control
[<portlist>] {rx_rate [no_limit | <value 64-1024000>] |
tx_rate [no_limit <value 64-1024000>]}
show bandwidth_control
{<portlist>}
Each command is listed, in detail, in the following sections.
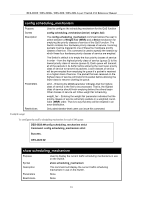
config scheduling
Purpose
Used to configure traffic scheduling for each of the Switch’s QoS
queues.
Syntax
config scheduling <class_id 0-3> {weight <value 1-55}
Description
The Switch contains four hardware priority classes of service per
device. The Switch’s default settings draw down the four hardware
classes of service in order, from the highest class (Class 3) to the
lowest class (Class 0). Starting with the highest priority class of
service (Class 3), the highest priority class of service will transmit all
of the packets and empty its buffer before allowing the next lower
priority class of service to transmit its packets. The next highest
priority class of service will empty before proceeding to the next
class of service and so on. Lower priority classes of service are
allowed to transmit only if
the higher priority classes of service in the
buffer are completely emptied. Packets in the higher priority classes
of service are always emptied before any in the lower priority
classes of service regardless of latency or volume of the lower
priority classes of service.
The default settings for QoS scheduling employ this strict priority
scheme to empty priority classes of service.
The
config scheduling
command can be used to specify the round
robin rotation by which these four hardware priority classes of
service are reduced.
The
weight
parameter allows you to specify the maximum number
of packets a given priority classes of service can transmit before
allowing the next lowest priority queue to begin transmitting its
packets. A value between 0 and 55 packets can be specified. For
example, if a value of 5 is specified, then the highest priority class of
service (queue 3) will be allowed to transmit 5 packets. Then the
next lower priority class of service (queue 2) will be allowed to
transmit 5 packets, and so on, until all of the classes of service have
transmitted 5 packets. The process will then repeat.
76