D-Link DSR-1000AC User Manual - Page 76
Network, Routing
 |
View all D-Link DSR-1000AC manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 76 highlights
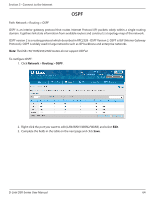
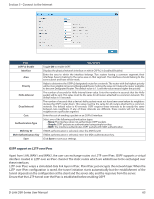
Section 5 - Connect to the Internet RIP Path: Network > Routing > RIP Dynamic routing using the Routing Information Protocol (RIP) is an Interior Gateway Protocol (IGP) that is common in LANs. With RIP this router can exchange routing information with other supported routers in the LAN and allow for dynamic adjustment of routing tables in order to adapt to modifications in the LAN without interrupting traffic flow. Note: The DSR-150/150N/250/250N routers do not support RIP. To configure RIP: 1. Click Network > Routing > RIP. 2. Complete the fields in the table below and click Save. Field Direction Version Description The RIP direction will define how this router sends and receives RIP packets. Select one of the following: • Both: The router both broadcasts its routing table and also processes RIP information received from other routers. This is the recommended setting in order to fully utilize RIP capabilities. • Out Only: The router broadcasts its routing table periodically but does not accept RIP information from other routers. • In Only: The router accepts RIP information from other routers, but does not broadcast its routing table. • None: The router neither broadcasts its route table nor does it accept any RIP packets from other routers. This effectively disables RIP. The RIP version is dependent on the RIP support of other routing devices in the LAN. • Disabled: This is the setting when RIP is disabled. • RIP-1: A class-based routing version that does not include subnet information. This is the most commonly supported version. • RIP-2: Includes all the functionality of RIPv1 plus it supports subnet information. Though the data is sent in RIP-2 format for both RIP-2B and RIP-2M, the mode in which packets are sent is different. RIP-2B broadcasts data in the entire subnet while RIP-2M sends data to multicast addresses. Save Note: If RIP-2B or RIP-2M is the selected version, authentication between this router and other routers (configured with the same RIP version) is required. MD5 authentication is used in a first/second key exchange process. The authentication key validity lifetimes are configurable to ensure that the routing information exchange is with current and supported routers detected on the LAN. Click Save to save your settings. D-Link DSR-Series User Manual 63