D-Link DSR-1000AC User Manual - Page 78
OSPF support on L2TP over IPsec
 |
View all D-Link DSR-1000AC manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 78 highlights
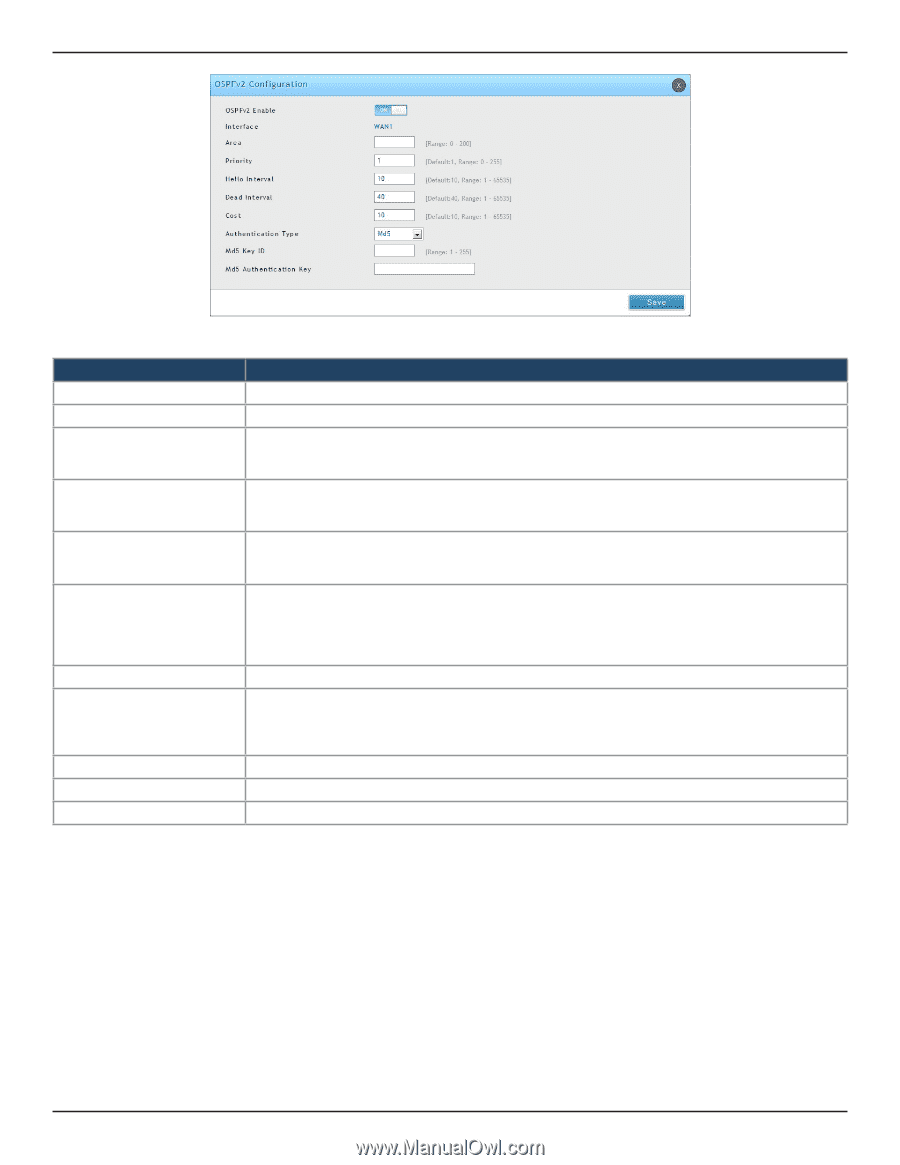
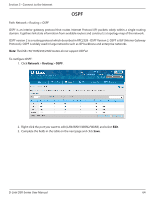
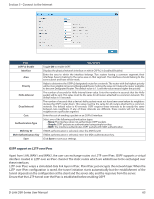
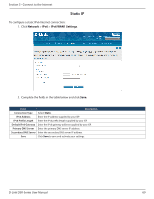
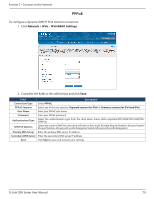
Section 5 - Connect to the Internet Field OSPFv2 Enable Interface Area Priority Hello Interval Dead Interval Cost Authentication Type Md5 Key ID Md5 Authentication Key Save Description Toggle ON to enable OSPF. Displays the physical network interface on which OSPFv2 is Enabled/Disabled. Enter the area to which the interface belongs. Two routers having a common segment; their interfaces have to belong to the same area on that segment. The interfaces should belong to the same subnet and have similar mask. Helps to determine the OSPFv2 designated router for a network. The router with the highest priority will be more eligible to become Designated Router. Setting the value to 0 makes the router ineligible to become Designated Router. The default value is 1. Lower the value means higher the priority. The number of seconds for Hello Interval timer value. Enter the number in seconds that the Hello packet will be sent. This value must be the same for all routers attached to a common network. The default value is 10 seconds. The number of seconds that a device's hello packets must not have been seen before its neighbors declare the OSPF router down. This value must be the same for all routers attached to a common network. The default value is 40 seconds. OSPF requires these intervals to be exactly the same between two neighbors. If any of these intervals are different, these routers will not become neighbors on a particular segment. Enter the cost of sending a packet on an OSPFv2 interface. Select one of the following authentication types: • None: The interface does not authenticate OSPF packets. • Simple: OSPF packets are authenticated using simple text key. • MD5: The interface authenticates OSPF packets with MD5 authentication. If MD5 authentication is selected, enter the MD5 key ID. If MD5 authentication is selected, enter the MD5 authentication key. Click Save to save your settings. OSPF support on L2TP over IPsec Apart from LAN, WAN1 and WAN2, the user can exchange routes via L2TP over IPsec. OSPF supports a virtual interface created in L2TP over an IPsec channel. The static routes which are added have to be exchanged over these interfaces. L2TP over IPsec wraps a stimulated data link layer in IPsec. Plain IPsec just encrypts the network layer. When the L2TP over IPsec configuration is saved, the tunnel initiation starts automatically but the establishment of the tunnel depends on the configuration at the client and the server side, and the response from the server. Ensure that the L2TP tunnel over the IPsec is established before enabling OSPF D-Link DSR-Series User Manual 65