HP Brocade 8/12c Fabric Watch Administrator's Guide v6.4.0 (53-1001770-01, Jun - Page 62
Fabric monitoring setting guidelines, Loss of E_Port
 |
View all HP Brocade 8/12c manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 62 highlights
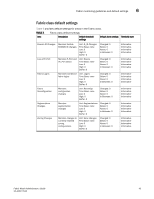
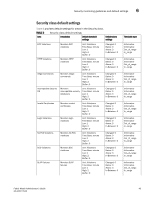
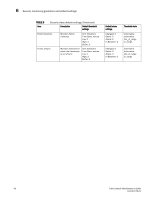
6 Fabric monitoring guidelines and default settings TABLE 3 Area Fabric class areas (Continued) Description Segmentation changes Tracks the cumulative number of segmentation changes. Segmentation changes occur because of one of the following: • Zone conflicts. • Incompatible link parameters. During E_Port and VE_Port initialization, ports exchange link parameters, and incompatible parameters result in segmentation. This is a rare event. • Domain conflicts. • Segmentation of the principal link between two switches. Zone changes Tracks the number of zone changes. Because zoning is a security provision, frequent zone changes might indicate a security breach or weakness. Zone change messages occur whenever there is a change in zone configurations. Fabric monitoring setting guidelines It is recommended that you leave the entire Fabric class in its default state (no alerts) for the following reasons. • Domain ID changes Plan and use strict change control practices to avoid Domain ID changes. • State changes SFP class areas and Port class (including E_Port and FOP_Port) areas are used to gather SFP state changes; therefore, don't change the default settings for the Fabric class. • Loss of E_Port Detect if an E_Port is down using the E_Port class areas. • Fabric logins In a large environment of numerous devices, this area is of no interest. • Fabric reconfiguration Fabric reconfigurations typically occur when new switches are added to a fabric, which is a planned activity, or when an upstream or downstream ISL fails, which is detected through the E_Port class areas. Since fabric reconfigurations are monitored elsewhere, don't change the default settings for the Fabric class. • Segmentation changes Segmentations only occur in the event of an entire switch failure. In this rare case, you can gather multiple reports from all the attached E_Ports of the link failures. • Zoning changes Zone changes are captured through the Audit facility in Fabric OS. All zone changes can be configured to be recorded in the RASlog, which is the recommended practice. 42 Fabric Watch Administrator's Guide 53-1001770-01