HP Brocade 8/12c Fabric Watch Administrator's Guide v6.4.0 (53-1001770-01, Jun - Page 67
SFP monitoring guidelines and default settings, SFP class areas, SFP monitoring setting guidelines
 |
View all HP Brocade 8/12c manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 67 highlights
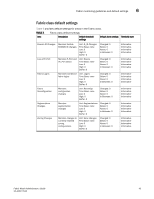
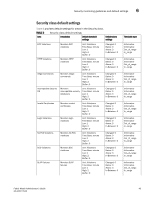
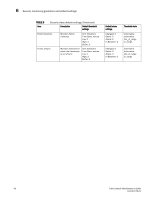
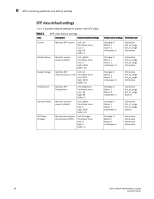
SFP monitoring guidelines and default settings 6 SFP monitoring guidelines and default settings The SFP class groups areas that monitor the physical aspects of SFPs. An SFP class alarm alerts you to an SFP malfunction fault. SFP performance monitoring is not supported on VE_Ports or VEX_Ports. NOTE SFPs connected to GbE ports are not monitored. SFP class areas Table 7 lists Product Name areas in the SFP class and describes each area. Configure the SFP class using the thConfig command. NOTE SFPs connected to GbE ports are not monitored. TABLE 7 Area SFP class areas Description Temperature Receive power (RXP) Transmit power (TXP) Current Voltage State Changes Measures the physical temperature of the SFP, in degrees Celsius. A high temperature indicates that the SFP might be in danger of damage. Measures the amount of incoming laser, in µwatts, to help determine if the SFP is in good working condition. If the counter often exceeds the threshold, the SFP is deteriorating. Measures the amount of outgoing laser, in µwatts. Use this to determine the condition of the SFP. If the counter often exceeds the threshold, the SFP is deteriorating. Measures the amount of supplied current to the SFP transceiver. Current area events indicate hardware failures. Measures the amount of voltage supplied to the SFP. If this value exceeds the threshold, the SFP is deteriorating. Indicates whether the state of the SFP is normal or faulty, on or off. A faulty or off state means that you must reinsert, turn on, or replace the SFP. Fabric Watch monitors only the digital diagnostic SFP. Note: SFPs connected to GbE ports are not monitored. SFP monitoring setting guidelines Use the SFP default settings. The default alarm configuration (log all alarms only to the error log) is sufficient. It is recommended that you do not allow alerts to go out as SNMP traps. If other Port class issues are reported, review the error log for any supporting data for SFP issues. Fabric Watch Administrator's Guide 47 53-1001770-01