HP Carrier-grade cc3300 Intel Server Management (ISM) Installation and User&am - Page 64
Command Line Interface CLI
 |
View all HP Carrier-grade cc3300 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 64 highlights
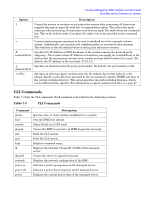
Intel Server Management (ISM) Installation and User's Guide Serial Data and the Command Line Interface • On Windows, if you start the network proxy in the foreground (the -f option), you can enter other options at the console's prompt. This is not true in Linux. Command syntax is as follows, and each option is described in Table 7-1. dpcproxy [-install] [-uninstall] [-?] [-h] [-f] [-p port] [-L] [-l language] [-d logfiledir] [-u] Table 7-1 The dpcproxy Command-line options Option -? or -h -install -uninstall -f -p port -L -l language -d logfiledir -u Description Displays a usage message and exits. If you specify either of these options, all other options and input text are ignored. Installs the proxy as a Windows service. You can also specify the other options to be used each time the proxy starts. Enter other options after the -install option. This option just installs the proxy and specifies behavior for when it is started-you must start the network proxy service after installing it. Removes the proxy from the Windows service control manager database. After removal, the proxy is no longer an installed service. Make sure to stop the service before you uninstall it. Runs the network proxy in the foreground. Specifies an alternate port at which the network proxy listens for incoming client connections. By default, the network proxy listens on port 623, which is a privileged port in most operating systems. Forces the network proxy to accept connections only from the local host address (127.0.0.1). This option prevents this instance of the network proxy from providing services to systems other than the local system. Localizes (displays in a specific language) messages and dates sent to a network proxy client. If you do not use this option, the network proxy detects the language from the Operating System. If a language is not specified on the command line the detected language is not a language supported by CLI; the network proxy defaults to English. Keeps a debug log file in the directory logfiledir. If you do not use this option, debug information is not logged. Turns off Serial over LAN data encryption for this instance of dpcproxy. With encryption off, all serial data transferred over the LAN is sent without encryption. Command Line Interface (CLI) The ISM Command Line Interface (CLI) lets you control a server from the command line rather than from a graphical user interface like PIC or DPC. You can enter CLI commands at a command prompt or from a script file to: • Start and stop Serial over LAN mode • Remotely power on or off a server • Remotely reset the server • Request machine identifiers • Change the boot device and device priority 64