Konica Minolta HP PageWide XL 5000 MFP User Guide - Page 73
Introduction, Control network protocols, Enable or disable network protocols, Front-panel menu items
 |
View all Konica Minolta HP PageWide XL 5000 MFP manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 73 highlights
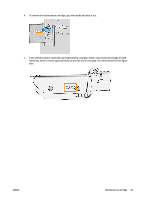
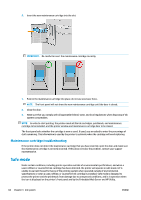
Introduction The printer provides a single RJ-45 connector port for a network connection. In order to meet Class B limits, the use of shielded I/O cables is required. The embedded Jetdirect print server supports connection to IEEE 802.3 10Base-T Ethernet, IEEE 802.3u 100Base-TX Fast Ethernet and 802.3ab 1000Base-T Gigabit Ethernet compliant networks. When connected and powered on, the printer auto-negotiates with your network to operate with a link speed of 10, 100, or 1000 Mbps, and to communicate using full- or half-duplex mode. However, you can manually configure the link using the printer's front panel, or through other configuration tools once network communication is established. The printer can support multiple network protocols simultaneously, including TCP/IPv4 and TCP/IPv6. For security, it includes features to control IP traffic to and from the printer and supports configuration of IP Security (IPsec) protocols. Control network protocols The printer can simultaneously support multiple network communication protocols. This allows network computers that may be using different protocols to communicate with the same printer. Each protocol may require some configuration before the printer can communicate on the network. For some protocols, required parameters are automatically sensed and user-specified settings are not needed. However, for other protocols, there may be many parameters to configure. Enable or disable network protocols If a network protocol is enabled, the printer may actively transmit on the network even when there are no computers on the network that use the protocol. This may increase network traffic. To eliminate unnecessary traffic, you can disable unused protocols. Disabling unused protocols lets you: ● Reduce network traffic by eliminating broadcast messages from unused protocols ● Provide better control over who prints to the printer by eliminating users from other networks who might route print jobs to this printer ● Display protocol-specific error conditions for enabled protocols only To disable unused protocols through the device's control panel menu, see Front-panel menu items on page 67. For other tools, such as system command access to the embedded Telnet server, see the HP Jetdirect Print Server Administrator's Guide for your print server model. Front-panel menu items To access the printer network configuration settings, go to the front panel and press Gigabit Ethernet. , then , then ENWW Introduction 67