Cisco 7941G Administration Guide - Page 24
Networking Protocol, Purpose, Usage Notes, as the Cisco Unified IP Phone - power
 |
UPC - 746320949420
View all Cisco 7941G manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 24 highlights
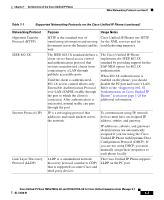
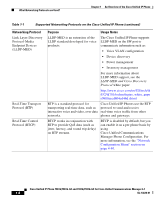
What Networking Protocols are Used? Chapter 1 An Overview of the Cisco Unified IP Phone Table 1-1 Supported Networking Protocols on the Cisco Unified IP Phone Networking Protocol Bootstrap Protocol (BootP) Cisco Discovery Protocol (CDP) Cisco Peer to Peer Distribution Protocol (CPPDP) Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) Purpose Usage Notes BootP enables a network device such as the Cisco Unified IP Phone to discover certain startup information, such as its IP address. If you are using BootP to assign IP addresses to the Cisco Unified IP Phone, the BOOTP Server option shows "Yes" in the network configuration settings on the phone. CDP is a device-discovery protocol that runs on all Cisco-manufactured equipment. Using CDP, a device can advertise its existence to other devices and receive information about other devices in the network. The Cisco Unified IP Phone uses CDP to communicate information such as auxiliary VLAN ID, per port power management details, and Quality of Service (QoS) configuration information with the Cisco Catalyst switch. CPPDP is a Cisco proprietary protocol used to form a peer to peer hierarchy of devices. CPPDP is also used to copy firmware or other files from peer devices to neighboring devices. CPPDP is used by the Peer Firmware Sharing feature. DHCP dynamically allocates and assigns an IP address to network devices. DHCP enables you to connect an IP phone into the network and have the phone become operational without your needing to manually assign an IP address or to configure additional network parameters. DHCP is enabled by default. If disabled, you must manually configure the IP address, subnet mask, gateway, and a TFTP server on each phone locally. Cisco recommends that you use DHCP custom option 150. With this method, you configure the TFTP server IP address as the option value. For additional supported DHCP configurations, refer to Cisco Unified Communications Manager System Guide. Cisco Unified IP Phone 7961G/7961G-GE and 7941G/7941G-GE for Cisco Unified Communications Manager 6.1 1-6 OL-14620-01