HP 6125G HP 6125G & 6125G/XG Blade Switches Layer 3 - IP Services Comm - Page 112
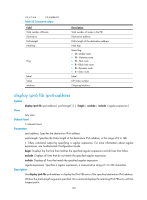
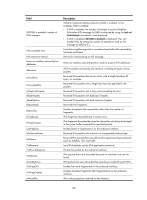
Table 25, Command output
 |
View all HP 6125G manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 112 highlights
ReasmOKs: InFragDrops: InFragTimeouts: OutFragFails: InUnknownProtos: InDelivers: OutRequests: OutForwDatagrams: InNoRoutes: InTooBigErrors: OutFragOKs: OutFragCreates: InMcastPkts: InMcastNotMembers: OutMcastPkts: InAddrErrors: InDiscards: OutDiscards: Table 25 Command output Field Vlan-interface2 current state Line protocol current state IPv6 is enabled link-local address Global unicast address(es) valid lifetime preferred lifetime Joined group address(es) MTU 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 Description Physical state of the interface: • Administratively DOWN-The VLAN interface is administratively down. The interface is shut down by using the shutdown command. • DOWN-The VLAN interface is administratively up but its physical state is down. No ports in the VLAN are up due to a connection or link failure. • UP-The administrative and physical states of the VLAN interface are both up. Link layer protocol state of the interface: • DOWN-The link layer protocol state of the VLAN interface is down. • UP-The link layer protocol state of the VLAN interface is up. IPv6 packet forwarding state of the interface. (After an IPv6 address is configured for an interface, IPv6 is automatically enabled on it. IPv6 packet forwarding is enabled in the example.) Link-local address configured for the interface. Global unicast addresses configured for the interface. Valid lifetime of the global unicast address obtained through stateless autoconfiguration. Preferred lifetime of the global unicast address obtained through stateless autoconfiguration. Addresses of multicast groups that the interface has joined. Maximum transmission unit of the interface. 105