HP 6125G HP 6125G & 6125G/XG Blade Switches Layer 3 - IP Services Comm - Page 167
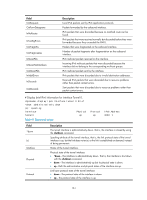
Table 40, Command output, Received IPv6 fragments.
 |
View all HP 6125G manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 167 highlights
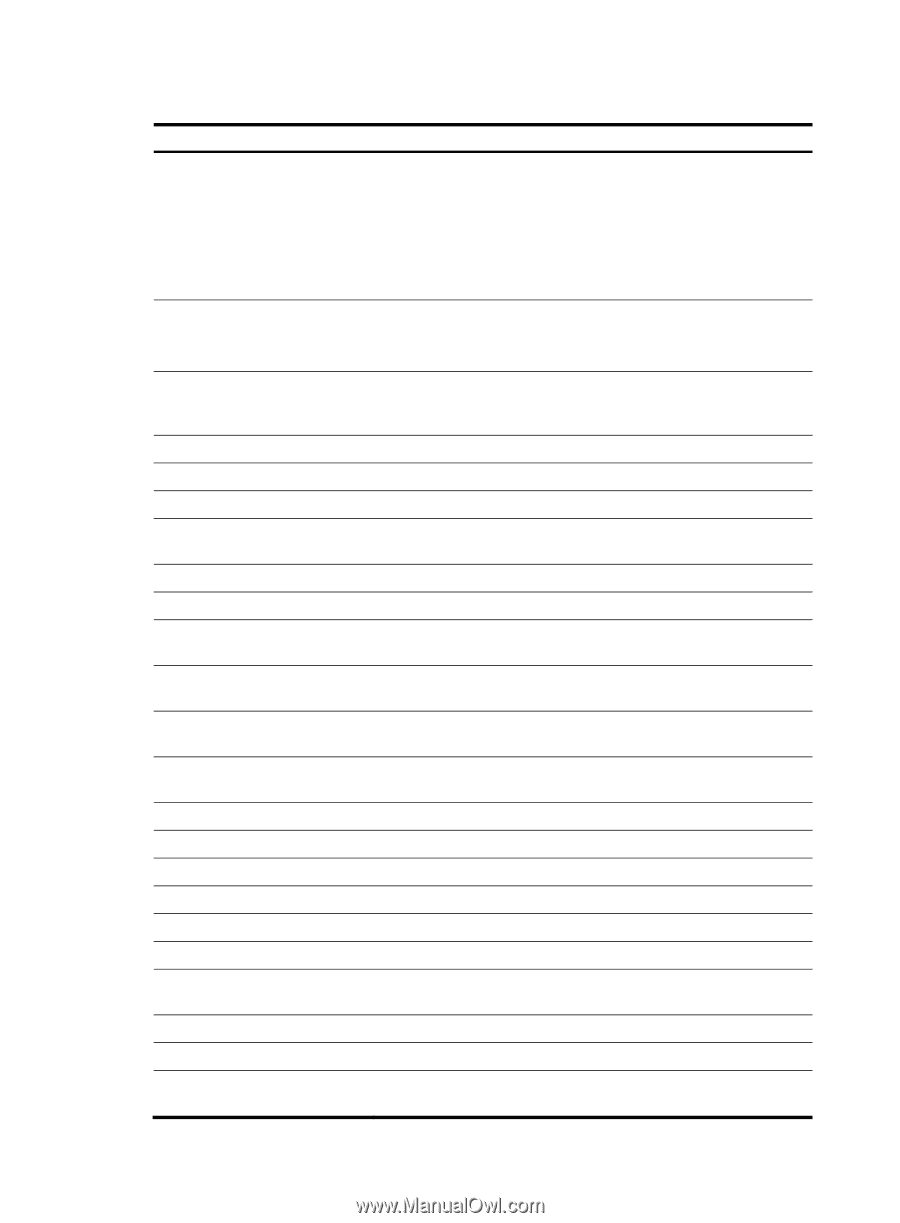
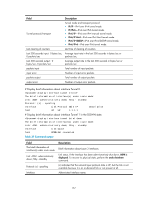
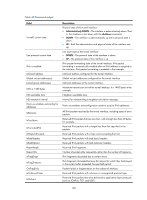
Table 40 Command output Field Tunnel0 current state Line protocol current state IPv6 is enabled link-local address Global unicast address(es) Joined group address(es) MTU is 1480 bytes ND reachable time ND retransmit interval Hosts use stateless autoconfig for addresses InReceives InTooShorts InTruncatedPkts InHopLimitExceeds InBadHeaders InBadOptions ReasmReqds ReasmOKs InFragDrops InFragTimeouts OutFragFails InUnknownProtos InDelivers Description Physical state of the tunnel interface: • Administratively DOWN-The interface is administratively down. That is, the interface is shut down with the shutdown command. • DOWN-The interface is administratively up but its physical state is down. • UP-Both the administrative and physical states of the interface are up. Link layer state of the tunnel interface: • DOWN-The protocol state of the interface is down. • UP-The protocol state of the interface is up. IPv6 packet forwarding state of the tunnel interface. IPv6 packet forwarding is automatically enabled after an IPv6 address is assigned to the interface. IPv6 packet forwarding is enabled in the example. Link-local address configured for the tunnel interface. Global unicast addresses configured for the tunnel interface. Multicast addresses of the tunnel interface. Maximum transmission unit of the tunnel interface. It is 1480 bytes in the example. Neighbor reachable time. Interval for retransmitting a neighbor solicitation message. Hosts use stateless autoconfiguration mode to acquire IPv6 addresses. All IPv6 packets received by the tunnel interface, including types of error packets. Received IPv6 packets that are too short, with a length less than 40 bytes, for example. Received IPv6 packets with a length less than that specified in the packets. Received IPv6 packets with a hop count exceeding the limit. Received IPv6 packets with bad basic headers. Received IPv6 packets with bad extension headers. Received IPv6 fragments. Number of packets after reassembly rather than the number of fragments. IPv6 fragments discarded due to certain errors. IPv6 fragments discarded because the interval for which they had stayed in the system buffer exceeded the specified period. Packets failed in fragmentation on the outbound interface. Received IPv6 packets with unknown or unsupported protocol type. Received IPv6 packets that were delivered to application layer protocols (such as ICMPv6, TCP, and UDP). 160