HP ProLiant 4500 Compaq ProLiant Cluster HA/F100 and HA/F200 Administrator Gui - Page 49
Example 2, for cluster-to-LAN communication. The Compaq Advanced Network Control
 |
View all HP ProLiant 4500 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 49 highlights
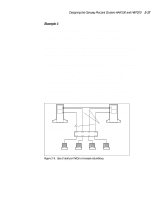
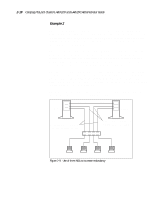
2-18 Compaq ProLiant Clusters HA/F100 and HA/F200 Administrator Guide Example 2 The second example configuration consists of three single-port NICs. One NIC is dedicated to intracluster communication. The other two NICs are used for cluster-to-LAN communication. The Compaq Advanced Network Control Utility is used to configure two of the NICs-one as the primary and one as the standby of a redundant pair. The interconnect is fully redundant when MSCS is configured to use the other network cards as backups for the interconnect. Failure of the primary interconnect path results in intracluster communications occurring over the primary NIC of the redundant pair. If the entire interconnect card fails, the cluster nodes will still have a working communication path. The cluster-to-LAN communication is fully redundant up to the network hub. With this configuration, even a failure of the primary NIC results only in the transfer of the network path to the standby NIC. Other than a failure of the network hub, any failure of any cluster network component will be resolved by the redundancy of this configuration. The primary disadvantage of this configuration as compared to Example 1 is that an additional card slot is used by the third NIC. Primary Interconnect Path Node 1 Node 2 Backup Cluster to LAN and Backup Interconnect Path Primary Cluster to LAN and Backup Interconnect Path Hub Clients Figure 2-9. Use of three NICs to increase redundancy