Dell EqualLogic PS6210XS EqualLogic Host Integration Tools for Microsoft Editi - Page 36
Determining the Number of iSCSI Sessions for a Volume Slice
 |
View all Dell EqualLogic PS6210XS manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 36 highlights
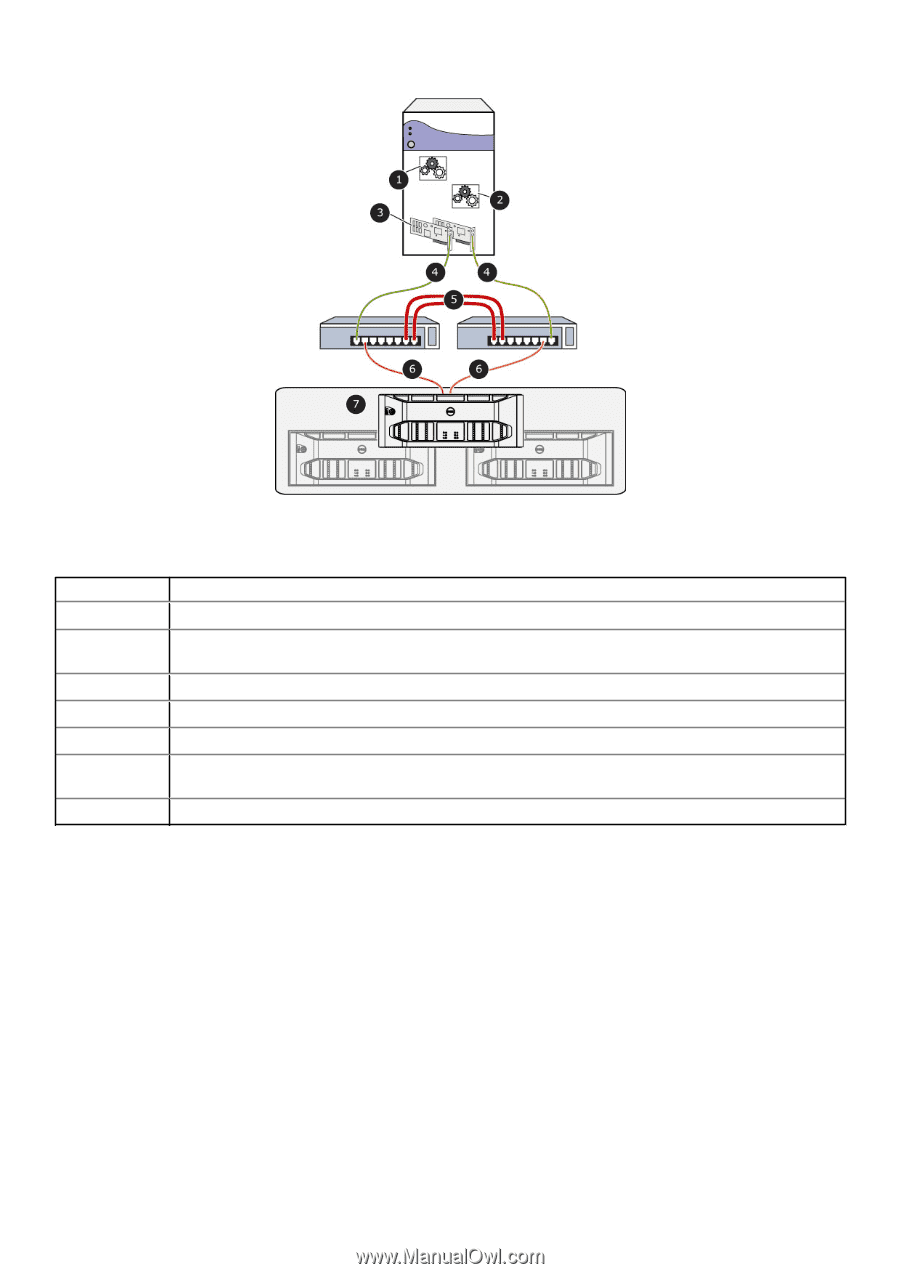
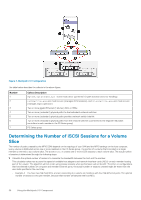
Figure 3. Multipath I/O Configuration The table below describes the callouts in the above figure. Number 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Callout Description eqldsm.sys or dcdsm.sys - kernel mode driver (performs I/O path selection and error handling) EHCMservice.exe user mode service (manages iSCSI sessions), and DC-HAService.exe user mode service (manages import operation) Two or more gigabit Ethernet (1 Gb/sec) NICs or HBAs Two or more (redundant) physical paths to dual redundant network switches Two or more (redundant) physical paths provide a network switch interlink Two or more (redundant) physical paths from the network switches (connected to the separate redundant controllers in each member in the PS Series group) PS Series group Determining the Number of iSCSI Sessions for a Volume Slice The number of paths created by the MPIO DSM depends on the topology of your SAN and the MPIO settings on the host computer. Every volume is distributed across one or more members in the PS Series group. The portion of a volume that is located on a single member is referred to as a volume slice. The EHCMservice creates one or more iSCSI sessions to each volume slice. The actual number of sessions is determined through the following steps: 1. Calculate the optimal number of sessions to maximize the bandwidth between the host and the member. This calculation takes into account the speed of available host adapters and network interface cards (NICs) on each member hosting part of the volume. The algorithm will not create unnecessary sessions when performance will not benefit. Therefore, in configurations that have limited numbers of computer and member Ethernet ports, the actual number of sessions created might be fewer than the user limits specified in the next step. • Example A-You have two 1Gb host NICs, and are connecting to a volume on members with four 1Gb Ethernet ports. The optimal number of sessions is two per member, because that number will saturate the host NICs. 36 Using the Multipath I/O Component