Dell PowerEdge C6105 Hardware Owner's Manual - Page 24
Post Error Code, Collecting System Event Log (SEL) for Investigation
 |
View all Dell PowerEdge C6105 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 24 highlights
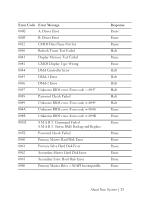
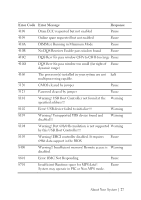
Post Error Code Collecting System Event Log (SEL) for Investigation Whenever possible, the BIOS will output the current boot progress codes on the video screen. Progress codes are 32-bit quantities plus optional data. The 32-bit numbers include class, subclass, and operation information. The class and subclass fields point to the type of hardware that is being initialized. The operation field represents the specific initialization activity. Based on the data bit availability to display progress codes, a progress code can be customized to fit the data width. The higher the data bit, the higher the granularity of information that can be sent on the progress port. The progress codes may be reported by the system BIOS or option ROMs. The Response section in the following table is divided into 3 types: 1 Warning or Not an error - The message is displayed on the screen. An error record is logged to the SEL. The system will continue booting with a degraded state. The user may want to replace the erroneous unit. 2 Pause - The message is displayed on the screen, an error is logged to the SEL, and user input is required to continue. The user can take immediate corrective action or choose to continue booting. 3 Halt - The message is displayed on the screen, an error is logged to the SEL, and the system cannot boot unless the error is resolved. The user needs to replace the faulty part and restart the system. Error Code Error Message Response 0000 Timer Error Pause 0003 CMOS Battery Low Pause 0004 CMOS Settings Wrong Pause 0005 CMOS Checksum Bad Pause 000B CMOS Memory Size Wrong Pause 000C RAM Read/Write Test Failed Pause 24 | About Your System