HP ML150 HP ProLiant ML100 Series Server User Guide - Page 22
Single- and dual-rank DIMMs (ML110 G6 servers), DIMM identification (ML110 G6 servers - g6 memory installation
 |
UPC - 884420743644
View all HP ML150 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 22 highlights
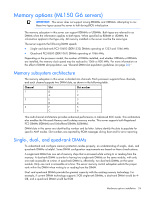
Channel Slot 1 C A 2 D B Slot number 1 2 3 4 This multi-channel architecture provides enhanced performance in Advanced ECC mode. This architecture also enables the Mirrored Memory and Lockstep memory modes. This server supports Unbuffered DIMMs (UDIMMs). DIMM slots in this server are identified by number and by letter. Letters identify the slots to populate for specific AMP modes. Slot numbers are reported by ROM messages during boot and for error reporting. Single- and dual-rank DIMMs (ML110 G6 servers) To understand and configure memory protection modes properly, an understanding of single-, dual-, and quad-rank DIMMs is helpful. Some DIMM configuration requirements are based on these classifications. A single-rank DIMM has one set of memory chips that is accessed while writing to or reading from the memory. A dual-rank DIMM is similar to having two single-rank DIMMs on the same module, with only one rank accessible at a time. A quad-rank DIMM is, effectively, two dual-rank DIMMs on the same module. Only one rank is accessible at a time. The server memory control subsystem selects the proper rank within the DIMM when writing to or reading from the DIMM. Dual-rank DIMMs provide the greatest capacity with the existing memory technology. For example, if current DRAM technology supports 2-GB single-rank DIMMs, a dual-rank DIMM would be 4-GB. DIMM identification (ML110 G6 servers) IMPORTANT: This server does not support mixing RDIMMs and UDIMMs. Attempting to mix these two types causes the server to halt during BIOS initialization. Hardware options installation 22