HP Xw8400 HP xw8400 Workstation - Service and Technical Reference Guide - Page 136
Error classes, Advanced > Chipset
 |
UPC - 883585271085
View all HP Xw8400 manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 136 highlights
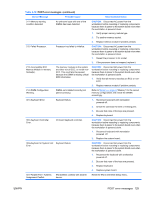
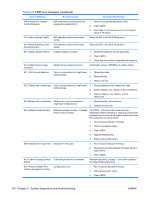
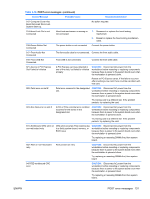
uncorrectable non-fatal errors are masked so they are logged, but will not generate an Err0. Unlike correctable non-fatal errors, the uncorrectable non-fatal errors will automatically force an F1 Boot prompt on the next reboot. Fatal errors are not masked. When errors are detected and not masked, they generate an Err0 signal. There are four ways to handle this type of error. ● Ignore (mask out the error) ● Generate an SMI which results in a reboot ● Generate an NMI which results in a crash ● Generate a Machine Check which results in a crash Default is to generate an SMI. Use the Advanced > Chipset option in the F10 Setup menu to control this type of error. Error classes There are two major classes of errors-fatal and non-fatal. All fatal errors generate error 922-Fatal error on (subsystem is identified) Non fatal errors generate a different error number for each subsystem and for correctable and uncorrectable error types: Error Class Type Description Device Result 922 Fatal Don't care Fatal error on Any Err0 923 Non-fatal Uncorrectable Non-fatal, uncorrectable PCI PCI or PCI-X F1 prompt error on (slot is identified) 924 Non-fatal Correctable Non-fatal, correctable PCI error PCI or PCI-X on (slot is identified) F1 optional 925 Non-fatal Uncorrectable Non-fatal, uncorrectable ESI error on (slot is identified) PCI or PCI-X F1 prompt 926 Non-fatal Correctable Non-fatal, correctable ESI error PCI or PCI-X on (slot is identified) F1 optional 927 Non-fatal Uncorrectable Non-fatal FSB error on (FSB is Front side bus F1 prompt identified) 928 Non-fatal Uncorrectable Non-fatal, uncorrectable FBD Memory error on (DIMM is identified) F1 prompt 929 Non-fatal Correctable Non-fatal, correctable FBD error Memory on (DIMM is identified) F1 optional 930 Non-fatal Correctable Non-fatal, Internal Northbridge Memory error controller F1 optional 126 Chapter 5 System diagnostics and troubleshooting ENWW