TP-Link TL-SG2424P TL-SG2424P V1 User Guide 1910010774 - Page 59
DHCP-DISCOVER Stage, DHCP-OFFER Stage, DHCP-REQUEST Stage
 |
View all TP-Link TL-SG2424P manuals
Add to My Manuals
Save this manual to your list of manuals |
Page 59 highlights
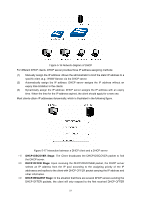
Figure 5-16 Network diagram of DHCP For different DHCP clients, DHCP server provides three IP address assigning methods: (1) Manually assign the IP address: Allows the administrator to bind the static IP address to a specific client (e.g.: WWW Server) via the DHCP server. (2) Automatically assign the IP address: DHCP server assigns the IP address without an expiry time limitation to the clients. (3) Dynamically assign the IP address: DHCP server assigns the IP address with an expiry time. When the time for the IP address expired, the client should apply for a new one. Most clients obtain IP addresses dynamically, which is illustrated in the following figure. Figure 5-17 Interaction between a DHCP client and a DHCP server (1) DHCP-DISCOVER Stage: The Client broadcasts the DHCP-DISCOVER packet to find the DHCP server. (2) DHCP-OFFER Stage: Upon receiving the DHCP-DISCOVER packet, the DHCP server selects an IP address from the IP pool according to the assigning priority of the IP addresses and replies to the client with DHCP-OFFER packet carrying the IP address and other information. (3) DHCP-REQUEST Stage: In the situation that there are several DHCP servers sending the DHCP-OFFER packets, the client will only respond to the first received DHCP-OFFER 51